Written by: Brendan on Blockchain Compiled by: Vernacular Blockchain
A few years ago, Ethereum was still Bitcoin's "little brother", known for decentralized finance (DeFi), pixelated NFTs, and creative smart contract experiments, and was far from the choice of "serious" investors. However, by 2025, Ethereum has become the focus of Wall Street.
Goldman Sachs perfectly embodied the mindset of traditional institutions in 2021, when they denigrated Ethereum as "too volatile and speculative" and called it "a solution in search of a problem." Their research team believes that smart contract technology is over-hyped, real-world applications are limited, and institutional clients have "no legitimate use cases" for programmable currencies. They are not alone, JPMorgan Chase calls it a "pet rock", and traditional asset management companies are even more shunned.
However, this view is as outdated as calling the Internet a "flash in the pan." Today, Goldman Sachs is quietly building Ethereum-based trading infrastructure, JPMorgan Chase is processing billions of dollars in transactions through its Ethereum-powered Onyx platform, and asset managers that once shied away are now launching Ethereum-related products at a rapid pace.
The real turning point came in 2024, when the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) finally approved an Ethereum spot ETF. This may not sound like an exciting dinner table topic, but it is significant. Unlike Bitcoin, which is simply classified as "digital gold", Ethereum is a difficult problem for regulators: how to regulate a programmable blockchain that supports everything from decentralized trading platforms to digital art markets? The fact that they finally solved this problem and released it is enough to say something about the direction of the industry.
ETF floodgates open
For years, there have been doubts about the regulatory clarity of Ethereum, especially the SEC's ambiguous attitude on whether Ethereum is a security. But the ETF approval marks an important signal: Ethereum has matured into an investable asset for pensions, asset managers, and even conservative family offices.
BlackRock was the first to launch the iShares Ethereum Trust, and frankly, watching the launch was like witnessing the "fear of missing out" (FOMO) of institutional investors in real time. Fidelity followed, Grayscale converted its existing products into ETFs, and suddenly every major asset manager launched an Ethereum product. But what's more striking is that these products are not limited to ordinary ETFs that track the price of ETH. Some also incorporate staking rewards, meaning that institutional investors can earn returns on their positions just like DeFi participants.
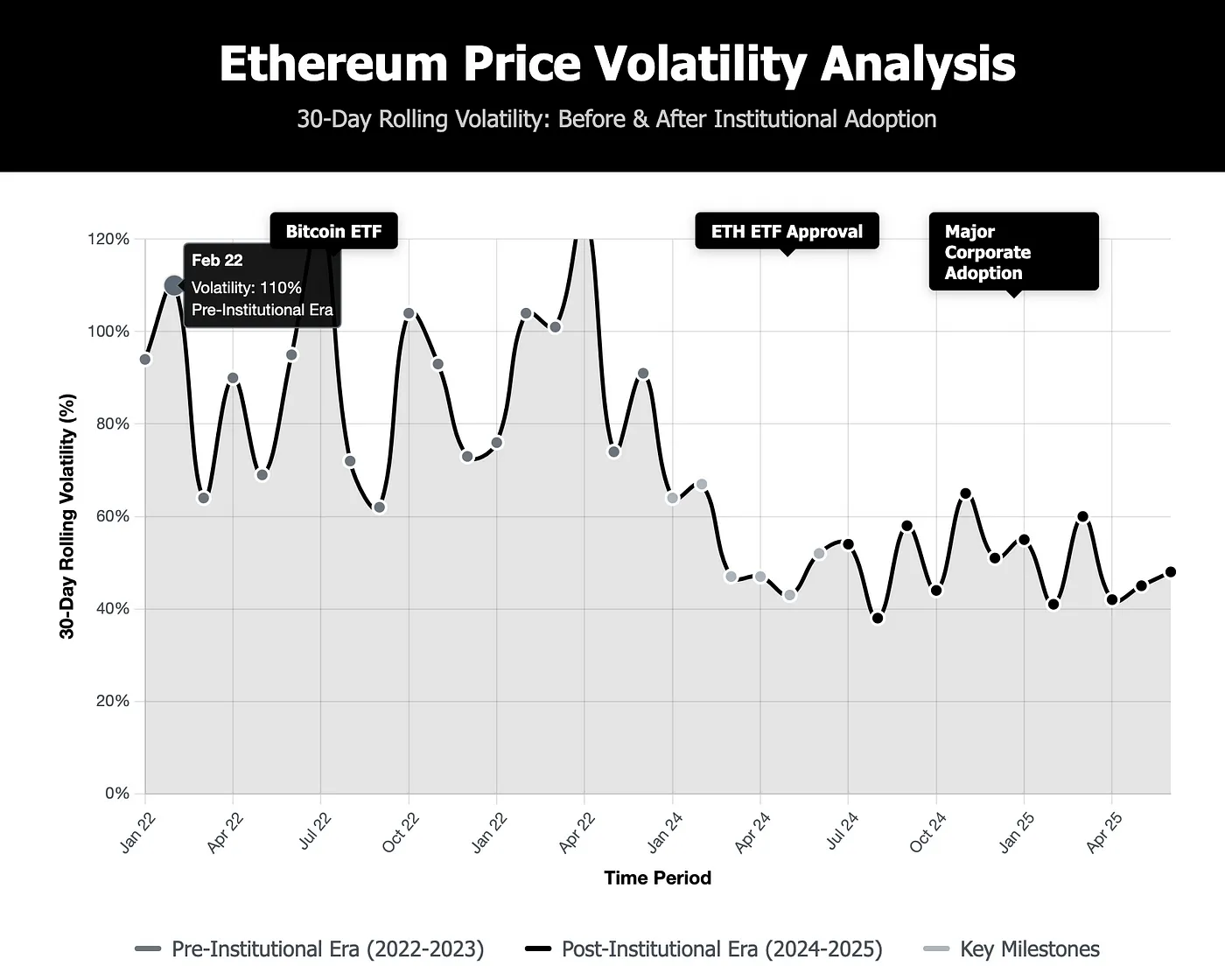
Visualization of Ethereum's price fluctuations before and after institutional adoption
Enterprise full embrace
What is really fascinating is how enterprises integrate Ethereum into actual business operations. This is not a speculative asset reserve like Bitcoin, but enterprises are building digital infrastructure on Ethereum because it can solve real problems.
The real value of Ethereum to institutions lies in its infrastructure as a programmable blockchain that can handle tokenized currencies, digital contracts, and complex financial workflows.
Institutions are quickly joining the wave:
Franklin Templeton, a firm with $1.5 trillion in assets under management, tokenized one of its mutual funds on Ethereum, and investors now hold digital shares on the blockchain, enjoying the benefits of transparency and 24/7 settlement.
JPMorgan, through its blockchain division Onyx, is testing tokenized deposits and asset swaps using Ethereum-compatible networks such as Polygon and their enterprise version of Ethereum Quorum.
Amazon AWS and Google Cloud now offer Ethereum node services, making it easy for enterprises to connect to the network without having to build their own infrastructure.
Microsoft is working with ConsenSys to explore enterprise use cases from supply chain tracking to compliance smart contracts.
These are no longer just the domain of crypto-native players. Traditional financial giants are waking up to the fast, secure, automated, unmediated financial services that Ethereum provides.
The conversation among CFOs at Fortune 500 companies has completely changed. Instead of questioning whether blockchain makes sense, they are asking how to apply smart contract automation to supplier payments, supply chain financing, and internal processes as quickly as possible. The efficiency gains are obvious.
The gaming and entertainment industries are particularly radical. Major game studios are tokenizing in-game assets, music platforms are automating royalty distribution, and streaming services are experimenting with decentralized content monetization. Ethereum's transparency and programmability have solved decades of problems in these industries almost overnight.
Why is Ethereum so attractive to institutions?

Ethereum allows assets (whether they are dollars, stocks, real estate or carbon credits) to be digitized, tokenized and programmatic. Combined with stablecoins (such as USDC or USDT) that mainly run on Ethereum, you suddenly have the cornerstones for building a whole new financial operating system.
Need instant settlement across borders?
Need programmable payments based on contractual milestones?
Need transparency without losing control?
Ethereum can do all of this and more.
Coupled with Layer 2 networks like Arbitrum and Optimism, these solutions extend Ethereum’s capacity, reduce fees, and dramatically increase speed. Many institutions choose to build on Layer 2 networks for increased efficiency while still leveraging Ethereum’s liquidity and security.
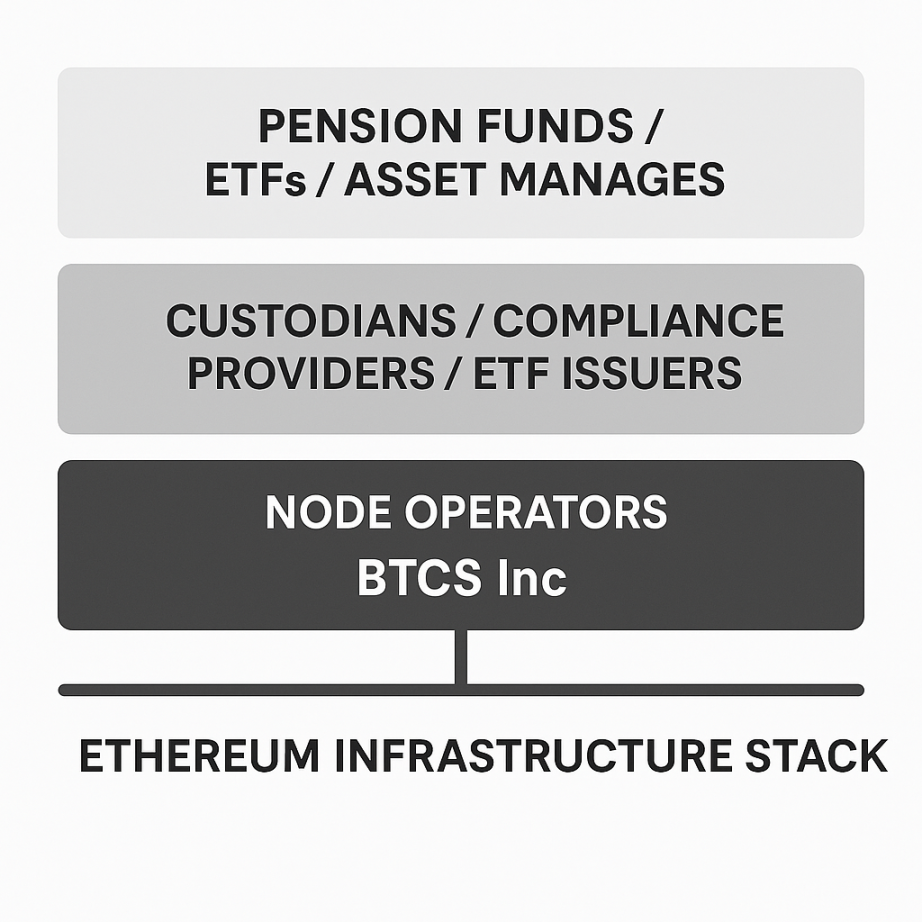
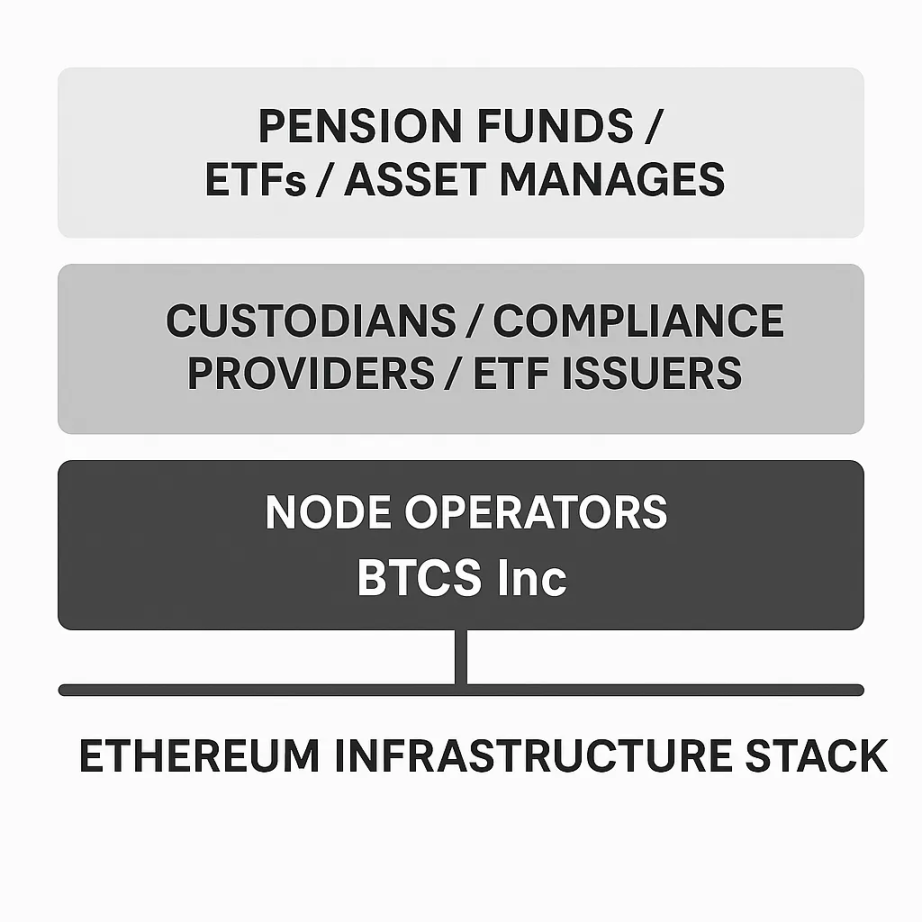
All of this institutional adoption is tied to the infrastructure layer that most people overlook. Companies like BTCS Inc are increasingly supporting the necessary infrastructure for traditional financial institutions to participate in Ethereum and products like the ETH ETF. BTCS focuses on operating secure enterprise-grade Ethereum validation nodes, maintaining network integrity and enabling institutions to participate in staking without having to deal with technical complexities. While they are not a custodian or ETF issuer, their validation node operations support the functionality and credibility of Ethereum, enhancing the network resilience and transparency required by institutional investors.
Looking to the future
What is the future trend? I think the direction is very clear. Ethereum is becoming the infrastructure layer for programmable finance. We are no longer talking about just crypto trading, but automated lending, programmable insurance, tokenized real estate, and supply chain finance that operates 24/7.
Integration with central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) is another huge opportunity. As countries develop digital currency strategies, many are considering Ethereum-compatible solutions to enable seamless interaction between government-issued digital currencies and the broader DeFi ecosystem.
More importantly, this institutional embrace is driving the regulatory clarity that the entire industry has long awaited. When major financial institutions build products around Ethereum, regulators have a strong incentive to develop workable frameworks rather than blanket restrictions.
We are witnessing a technology that started as an experimental platform gradually become critical financial infrastructure. The approval of an ETF is significant, but it is just the beginning. The real story is how Ethereum will fundamentally change the way financial services are operated, the way enterprises manage operations, and the way value flows in the global economy.
To be honest, I think we are still in the early stages of this transformation. Current institutional adoption is just the beginning of the large-scale integration of programmable money and traditional finance.
 YouQuan
YouQuan








