16% of Web3 companies use .io
16% of Web3 companies use .io. ccTLDs have been removed five times in history.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
Compiled by: Golden Finance; Source: Chain Tea House, MIIX Capital, Binance, Golden Finance
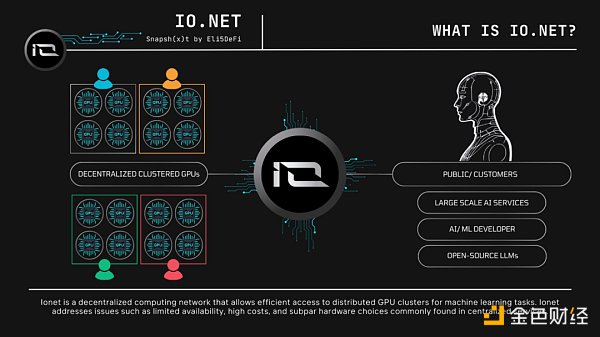
On June 6, 2024, Binance announced that Binance Newcoin Mining has now launched the 55th project IO.NET (IO), a decentralized artificial intelligence computing and cloud platform.
io.net is a distributed GPU system based on Solana, Render, Ray, and Filecoin, designed to use distributed GPU resources to solve computing challenges in the fields of AI and machine learning.
io.net solves the problem of insufficient computing resources by aggregating underutilized computing resources such as independent data computing centers, cryptocurrency miners, and excess GPUs of crypto projects such as Filecoin and Render, enabling engineers to obtain a large amount of computing power in an easily accessible, customizable and low-cost system.
In addition, io.net introduces a distributed physical infrastructure network (depin), combining resources from various providers, enabling engineers to obtain a large amount of computing power in a customizable, cost-effective and easy-to-implement manner. io cloud now has more than 95,000 GPUs and more than 1,000 CPUs, supports fast deployment, selects hardware, geography, and provides a transparent payment process.
Token Name: IO.NET (IO)
Maximum Token Supply: 800,000,000 IO
Initial Circulation: 95,000,000 IO (19% of the total initial token supply)
Total Mining Amount: 20,000,000 IO (4% of the total initial token supply)
BNB Mining Pool: A total of 17,000,000 IO can be mined IO (accounting for 85%)
FDUSD mining pool: a total of 3,000,000 IO can be mined (accounting for 15%)
Mining time: 08:00 on June 7, 2024 to 07:59 on June 11, 2024, Eastern Time
io.net's decentralized resource aggregation is one of its core features, which enables the platform to utilize decentralized GPU resources around the world to provide the necessary computing support for AI and machine learning tasks. The goal of this resource aggregation strategy is to optimize resource usage, reduce costs, and provide wider accessibility.

Here is a detailed introduction:
3.1.1 Advantages
Cost-effectiveness: By leveraging underutilized GPU resources on the market, io.net is able to provide lower-cost computing power than traditional cloud services. This is especially important for data-intensive AI applications, which often require a large amount of computing resources, and traditional methods can be costly.
Scalability and flexibility: The decentralized model allows io.net to easily expand its resource pool without relying on a single vendor or data center. This model provides users with the flexibility to choose the resources that best suit their task requirements.
3.1.2 How it works
Diversity of resource sources: io.net aggregates GPU resources from multiple sources, including independent data centers, individual cryptocurrency miners, and excess resources from other crypto projects such as Filecoin and Render.
Technical implementation: The platform uses blockchain technology to track and manage these resources, ensuring transparency and fairness in resource allocation. Blockchain technology also helps automate payments and incentives to users who contribute additional computing power to the network.
3.1.3 Specific steps
Resource discovery and registration: Resource providers (such as GPU owners) register their devices with the io.net platform. The platform verifies the performance and reliability of these resources to ensure that they meet specific standards and requirements.
Resource Pooling: Verified resources are added to a global resource pool and are available for rent by platform users. The distribution and management of resources are automatically executed through smart contracts, ensuring transparency and efficiency of the process.
Dynamic Resource Allocation: When a user initiates a computing task, the platform dynamically allocates resources based on the requirements of the task (such as computing power, memory, network bandwidth, etc.). The allocation of resources takes into account cost efficiency and geographical location, optimizing the speed and cost of task execution.
io.net's dual token economic system is one of the core features of its blockchain network, designed to incentivize network participants and ensure the efficiency and sustainability of the platform's operations. This system includes two tokens: $IO and $IOSD, each of which plays a unique role. The structure and function of this economic system are described in detail below.
3.2.1 $IO Token
$IO is the main functional token of the io.net platform, used for a variety of network transactions and operations. Its main uses include:
Payment and Fees: Users use $IO to pay for the rental of computing resources, including GPU usage fees. In addition, $IO is also used to pay for various services and fees on the network.
Resource Incentives: $IO tokens are issued as rewards to users who provide GPU computing power or participate in maintaining the network, incentivizing them to continue to contribute resources.
Governance: $IO token holders can participate in the governance decisions of the io.net platform, including voting rights, and influence the future development direction and policy adjustments of the platform.
3.2.2 $IOSD Token
$IOSD is a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, designed to provide a stable value storage and transaction medium for the io.net platform. The main functions are as follows:
Value stability: The value of $IOSD is fixed to the US dollar at a 1:1 ratio, providing users with a payment method that avoids crypto market fluctuations.
Easy transactions: Users can use $IOSD to pay platform fees, such as computing resource fees, ensuring the stability and predictability of transactions in value.
Fee coverage: Certain network operations or transaction fees can be paid with $IOSD, simplifying the fee settlement process.
3.2.3 How the Dual Token System Works
io.net’s dual token system interacts in several ways to support the operation and growth of the network:
Resource Provider Incentives: Resource providers (such as GPU owners) receive $IO tokens in return for contributing their devices to the network. These tokens can be used to further purchase computing resources, or traded on the market.
Fee Payments: Users pay for the use of computing resources with $IO or $IOSD. Choosing $IOSD avoids the risks of cryptocurrency volatility.
Economic Activity Incentives: Through the circulation and use of $IO and $IOSD, the io.net platform is able to stimulate economic activity and increase the liquidity and participation of the network.
Governance Participation: $IO tokens also act as governance tokens, enabling holders to participate in the platform’s governance process, such as proposals and voting decisions.
IO.NET's dynamic resource allocation and scheduling is one of the core functions of the platform. The key lies in efficiently managing and optimizing the use of computing resources to meet the diverse computing needs of users. This system ensures that computing tasks can be executed on the most appropriate resources in an intelligent and automated manner, while maximizing resource utilization and performance.
The following is a detailed introduction to each aspect of this mechanism:
3.3.1 Dynamic Resource Allocation Mechanism
1. Resource Identification and Classification:
When a resource provider connects its GPU or other computing resources to the io.net platform, the system first identifies and classifies these resources. This includes evaluating their performance indicators such as processing speed, memory capacity, network bandwidth, etc.
These resources are then tagged and archived so that they can be dynamically allocated according to the needs of different tasks.
2. Demand matching:
When users submit computing tasks to io.net, they need to specify the requirements of the task, such as the required computing power, memory size, budget constraints, etc.
The platform's scheduling system analyzes these requirements and selects matching resources from the resource pool.
3. Intelligent scheduling algorithm:
Advanced algorithms are used to automatically match the most suitable resources with the submitted tasks. These algorithms take into account the performance, cost efficiency, geographical location (to reduce latency) of the resources, and the specific preferences of the users.
The scheduling system also monitors the real-time status of resources, such as availability and load, to dynamically adjust resource allocation.
3.3.2 Scheduling and Execution
1. Task Queues and Priority Management:
All tasks are queued according to priority and submission time. The system processes the task queue according to preset or dynamically adjusted priority rules.
Urgent or high-priority tasks can get a quick response, while long-term or cost-sensitive tasks may be executed during low-cost periods.
2. Fault Tolerance and Load Balancing:
The dynamic resource allocation system includes a fault-tolerant mechanism to ensure that even when some resources fail, tasks can be smoothly migrated to other healthy resources for continued execution.
Load balancing technology ensures that no single resource is overloaded and optimizes the performance of the entire network by properly distributing task loads.
3. Monitoring and Adjustment:
The system continuously monitors the execution status of all tasks and the operating status of resources. This includes real-time analysis of key performance indicators such as task progress and resource consumption.
Based on this data, the system may automatically readjust resource allocation to optimize task execution efficiency and resource utilization.
3.3.3 User Interaction and Feedback
Transparent User Interface: io.net provides an intuitive user interface that allows users to easily submit tasks, view task status, and adjust requirements or priorities.
Feedback Mechanism: Users can provide feedback on the results of task execution, and the system adjusts the resource allocation strategy for future tasks based on the feedback to better meet user needs.

IO Cloud is designed to simplify the deployment and management of decentralized GPU clusters, providing machine learning engineers and developers with scalable and flexible access to GPU resources without major hardware investments. This platform provides an experience similar to traditional cloud services, but with the advantages of a decentralized network.
Highlights:
Scalability and Economy: Designed to be the most cost-effective GPU cloud, it can reduce the cost of AI/ML projects by up to 90%.
Integration with IO SDK: Enhance AI project performance through seamless integration to create a unified high-performance environment.
Global Coverage: Distributed GPU resources, optimized for machine learning serving and inference, similar to a CDN.
RAY Framework Support: Scalable Python application development with the RAY distributed computing framework.
Exclusive Features: Provides private access to the OpenAI ChatGPT plugin for easy deployment of training clusters.
Crypto Mining Innovation: Seeking to revolutionize crypto mining by supporting the machine learning and AI ecosystem.
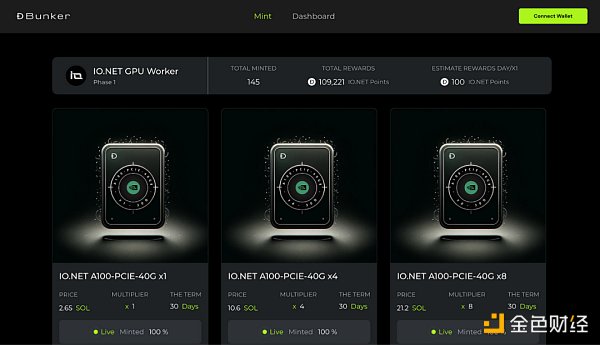
IO Worker is designed to simplify and optimize provisioning operations for WebApp users. This includes user account management, real-time activity monitoring, temperature and power consumption tracking, installation support, wallet management, security, and profitability analysis.
Highlights:
Worker Home Page: Provides a dashboard for real-time monitoring of connected devices, with the ability to delete and rename devices.
Device Details Page: Displays comprehensive device analytics, including traffic, connection status, and work history.
Earnings & Rewards Page: Tracks earnings and work history, with transaction details accessible on SOLSCAN.
Add New Device Page: Simplifies the device connection process, enabling fast and easy integration.
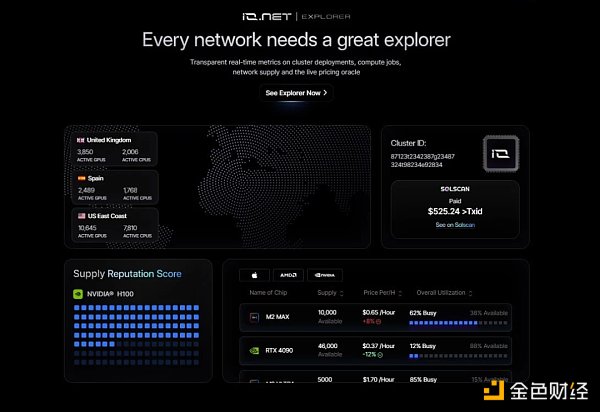
IO Explorer is designed as a comprehensive platform to provide users with deep insights into the operations of the io.net network, similar to how blockchain explorers provide transparency into blockchain transactions. Its main goal is to enable users to monitor, analyze and understand the details of the GPU Cloud, ensuring full visibility into network activity, statistics and transactions, while protecting the privacy of sensitive information.
Benefits:
Browser Homepage: Provides insights into supply, verified suppliers, number of active hardware and real-time market pricing.
Cluster Page: Displays public information of clusters deployed in the network, as well as real-time metrics and booking details.
Device Page: Displays public details of devices connected to the network, providing real-time data and transaction tracking.
Real-time Cluster Monitoring: Provides instant insights into cluster status, health and performance, ensuring users have the latest information.
IO-SDK is the foundational technology of Io.net, derived from a fork of Ray technology. It enables tasks to run in parallel and handle different languages, and is compatible with major machine learning (ML) frameworks, making IO.NET flexible and efficient for a variety of computing needs. This setup, coupled with a set of well-defined technologies, ensures that IO.NET Portal can meet today's needs and adapt to future changes.
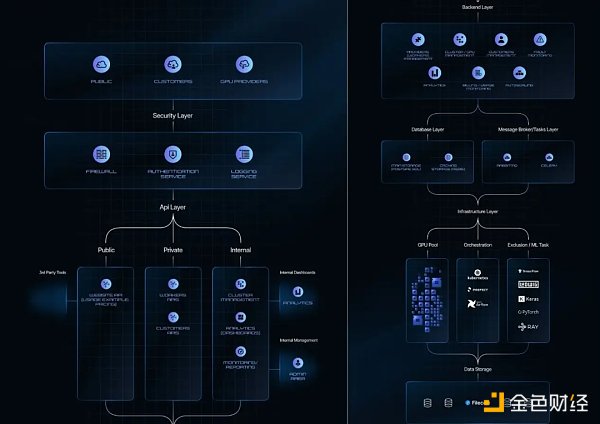
Application of multi-layer architecture
User interface: Serves as the visual front end for users, including the public website, customer area, and GPU provider area. The design is intuitive and user-friendly.
Security layer: Ensures the integrity and security of the system, including network protection, user authentication, and activity logging.
API layer: Serves as a communication center for websites, providers, and internal management, facilitating data exchange and operations.
Backend layer: The core of the system, handling operations such as cluster/GPU management, customer interaction, and automatic scaling.
Database layer: stores and manages data, with primary storage for structured data and cache for temporary data.
Task layer: manages asynchronous communications and tasks, ensuring efficiency of execution and data flow.
Infrastructure layer: infrastructure, including GPU pools, orchestration tools, and execution/ML tasks, equipped with powerful monitoring solutions.
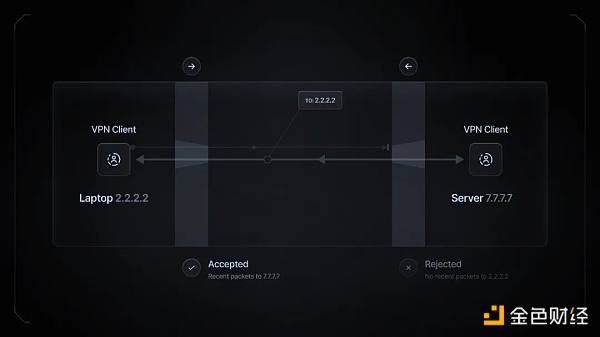
Use reverse tunneling technology to create a secure connection from the client to the remote server, enabling engineers to bypass firewalls and NAT for remote access without complex configuration.
Workflow: IO Worker connects to the intermediate server (io.net server). The io.net server then listens for connections from IO Worker and engineer machines, facilitating data exchange through reverse tunnels.
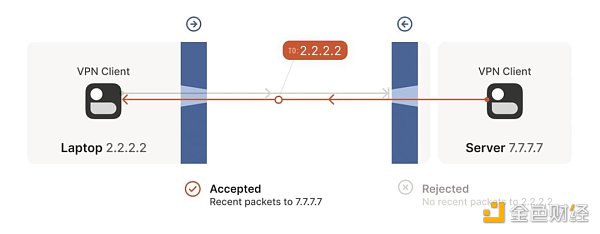
Application in io.net
Engineers connect to IO Workers through the io.net server, simplifying remote access and management without network configuration challenges.
Benefits:
Ease of access: Directly access IO Workers and eliminate network barriers.
Security: Ensure protected communications and maintain data privacy.
Scalability and flexibility: Effectively manage multiple IO Workers in different environments.
IO Network adopts a mesh VPN architecture to provide ultra-low latency communication between antMiner nodes.
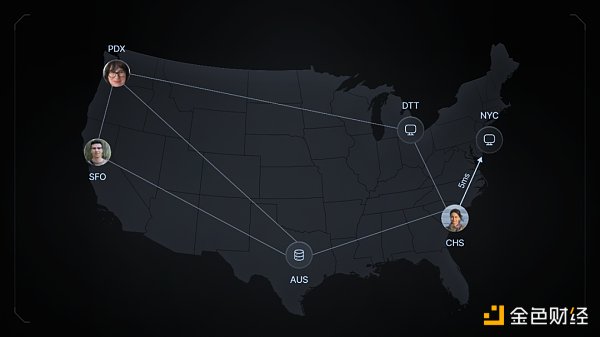
Mesh VPN Network:
Decentralized Connectivity: Unlike the traditional star model, mesh VPN directly connects nodes, providing enhanced redundancy, fault tolerance, and load distribution.
Advantages: Strong resistance to node failures, strong scalability, low latency, and better traffic distribution.
Benefits of io.net:
Direct connections reduce latency and optimize application performance.
No single point of failure, the network can still operate even if a single node fails.
Enhanced user privacy by making data tracking and analysis more challenging.
The addition of new nodes does not affect performance.
Resource sharing and processing are more efficient between nodes.
GPU renters (also known as users), such as machine learning engineers who want to purchase GPU computing power on the IOG network. These engineers can use $IO to deploy GPU clusters, cloud gaming instances, and build Unreal Engine 5 (and similar) pixel streaming applications. Users also include individual consumers who want to perform serverless model inference on BC8.ai and the hundreds of applications and models that io.net will host in the future.
GPU owners (also known as suppliers), such as independent data centers, crypto mining farms, and professional miners, hope to provide underutilized GPU computing power on the IOG network and profit from it.
IO coin holders (also known as the community) participate in providing cryptoeconomic security and incentives to coordinate mutual benefits and penalties between parties to promote the development and adoption of the network.
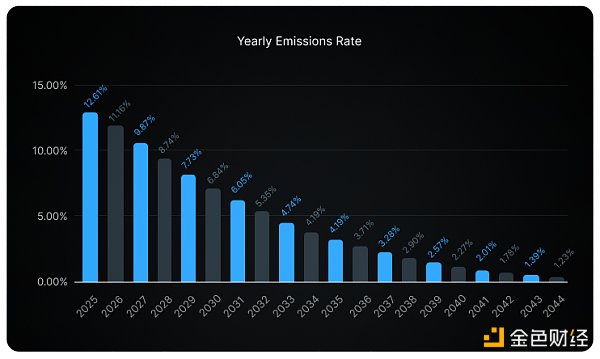
2024-2025: During these two years, 6,000,000 $IO tokens will be released each year.
2026-2027: Starting in 2026, the annual release will be halved to 3,000,000 $IO tokens.
2028-2029: The release will continue to halve, with 1,500,000 $IO tokens released each year.
io.net is a decentralized computing network based on the Solana blockchain, focusing on providing powerful computing power by integrating underutilized GPU resources. This project is mainly in the following track areas:
1. Decentralized Computing
io.net has built a decentralized physical infrastructure network (Depin) that utilizes GPU resources from different sources (such as independent data centers, crypto miners). This decentralized approach aims to optimize the utilization of computing resources and reduce costs while increasing accessibility and flexibility.
2. Cloud Computing
Although io.net adopts a decentralized approach, it provides services similar to traditional cloud computing, such as GPU cluster management and scalability for machine learning tasks. io.net aims to create an experience similar to traditional cloud services, but takes advantage of decentralized networks to provide more efficient and cost-effective solutions.
3. Blockchain Applications
As a project based on blockchain technology, io.net uses the characteristics of blockchain, such as security and transparency, to manage resources and transactions in the network.
Projects similar to io.net in terms of functionality and goals include:
Golem: It is also a decentralized computing network where users can rent or lease unused computing resources. Golem is committed to creating a global supercomputer.
Render: It uses decentralized networks to provide graphics rendering services. Render uses blockchain technology to enable content creators to access more GPU resources, thereby accelerating the rendering process.
iExec RLC: This project creates a decentralized market that allows users to rent out their computing resources. iExec supports various types of applications, including data-intensive applications and machine learning workloads, through blockchain technology.
Scalability: io.net has designed a highly scalable platform to meet customers' bandwidth needs and enable teams to easily scale workloads on GPU networks without large-scale adjustments.
Batch Inference and Model Serving: The platform supports parallelized inference on data batches, allowing machine learning teams to deploy workflows on distributed GPU networks.
Parallel Training: To overcome memory limitations and sequential workflows, io.net leverages distributed computing libraries to parallelize training tasks on multiple devices.
Parallel Hyperparameter Tuning: Leveraging the inherent parallelism of hyperparameter tuning experiments, io.net optimizes scheduling and search patterns.
Reinforcement Learning (RL): Leveraging open source reinforcement learning libraries, io.net supports highly distributed RL workloads and provides a simple API.
Instant Accessibility: Unlike the long deployment of traditional cloud services, io.net Cloud provides instant access to GPU provisioning, enabling users to launch their projects in seconds.
Cost Efficiency: io.net is designed to be an affordable platform suitable for different categories of users. Currently, the platform is about 90% more cost-effective than competing services, providing significant savings for machine learning projects.
High Security and Reliability: The platform promises best-in-class security, reliability, and technical support, ensuring a secure and stable environment for machine learning tasks.
Ease of Implementation: io.net Cloud eliminates the complexity of building and managing infrastructure, enabling any developer and organization to seamlessly develop and scale AI applications.
1. Technical Complexity and User Adoption
Challenges: While decentralized computing offers significant cost and efficiency advantages, its technical complexity may pose a large entry barrier for non-technical users. Users need to understand how to operate a distributed network and how to effectively utilize distributed resources.
Impact: This may limit the widespread adoption of the platform, especially among user groups that are less familiar with blockchain and distributed computing.
2. Network Security and Data Privacy
Challenges: Although blockchain offers enhanced security and transparency, the openness of decentralized networks may make them more vulnerable to cyber attacks and data leaks.
Impact: This requires io.net to continuously strengthen its security measures to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of user data and computing tasks, which is key to maintaining user trust and platform reputation.
3. Performance and reliability
Challenges: Although io.net strives to provide efficient computing services through decentralized resources, coordination between hardware resources in different geographical locations and of different quality may bring challenges in performance and reliability.
Impact: Any performance issues caused by hardware mismatch or network latency may affect customer satisfaction and the overall effect of the platform.
4. Scalability of scale
Challenges: Although io.net has designed a highly scalable network, it is still a huge technical challenge to effectively manage and expand decentralized resources around the world in actual operations.
Impact: This requires continuous technological innovation and management improvements to keep the network stable and responsive in the face of rapidly growing user and computing needs.
5. Competition and market acceptance
Challenges: io.net is not without competition in the blockchain and decentralized computing market. Other platforms such as Golem, Render, and iExec are also providing similar services, and rapid changes in the market may quickly change the competitive situation.
Impact: In order to remain competitive, io.net needs to continue to innovate and improve the uniqueness and value of its services to attract and retain users.
The emergence of io.net fills the gap in the field of decentralized computing and provides users with a novel and potential way of computing. With the continuous development of fields such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, the demand for computing resources is also increasing, so io.net has high market potential and value.
On the other hand, although the market has given io.net a high valuation of $1 billion, its products have not been tested by the market, and there are uncertain risks in terms of technology. Whether it can effectively match its supply and demand relationship is also a key variable that determines whether its subsequent market value can reach new highs. From the current situation, the results of the io.net platform on the supply side have already begun to show, but it has not yet fully exerted its strength on the demand side, resulting in the current platform's overall GPU resources not being fully utilized. How to more effectively mobilize the demand for GPU resources is a challenge that the team has to face.
If io.net can quickly access market demand and does not encounter or encounter major risks and technical problems during the operation process, with its AI+DePIN entity business attributes, its overall business will start the growth flywheel and become the most dazzling project product in the Web3 field. This also means that io.net will be a high-quality investment target for the branch. Let us continue to follow up and observe and verify carefully.
16% of Web3 companies use .io. ccTLDs have been removed five times in history.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceBitFuFu achieved total revenue of $129.4 million in the second quarter of 2024, an increase of 69.7% from $76.3 million in the same period of 2023.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceShiba Inu faces a 12% overnight plunge, prompting investors to shift towards Binance Coin and Everlodge amid mysterious market dynamics. While Shiba Inu struggles, Binance Coin surges past $300, and Everlodge's disruptive DeFi approach to holiday property ownership gains traction with potential high returns.
 Joy
JoyThe creation of Bitcoin paved the way for a new age of finance and a surge of new cryptocurrency projects ...
 Bitcoinist
BitcoinistRoboApe (RBA) is a fantastic new token that is clearing on its path to make the world of the cryptocurrency ...
 Bitcoinist
BitcoinistAltcoins are a unique breed of digital currencies. Most altcoins do not attempt to solve anything new or revolutionary, but ...
 Bitcoinist
BitcoinistThe rise in the popularity of cryptocurrencies left many in the financial services world surprised. No one had expected a ...
 Bitcoinist
BitcoinistRoboApe (RBA) is an upcoming meme token that is ready to transform the crypto world with a wide range of ...
 Bitcoinist
BitcoinistIt could be a dream come true for investors to be part of the crypto boom of 2022. The crypto ...
 Bitcoinist
BitcoinistBinance CEO Changpeng Zhao shared some crypto recommendations following the collapse of TerraForm Labs LUNA and UST Coins resulting in ...
 Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist