Author: 0xEdwardyw, Source: TokenInsight
This article explores the core advantages of the three major DeFi protocols Uniswap, Aave and Maker (Sky), and analyzes their potential for integration with traditional finance (TradFi) under the new US regulatory system
1. Regulatory shift opens the door to the integration of DeFi and traditional finance: New SEC Chairman Paul Atkins has promoted a fundamental shift in US crypto regulation, explicitly supporting self-custody rights, determining that pledges do not constitute securities activities, and advocating transparent, rule-based supervision, promoting mechanisms such as "innovation exemptions", and releasing the institutional dividends of cooperation between DeFi and traditional finance.
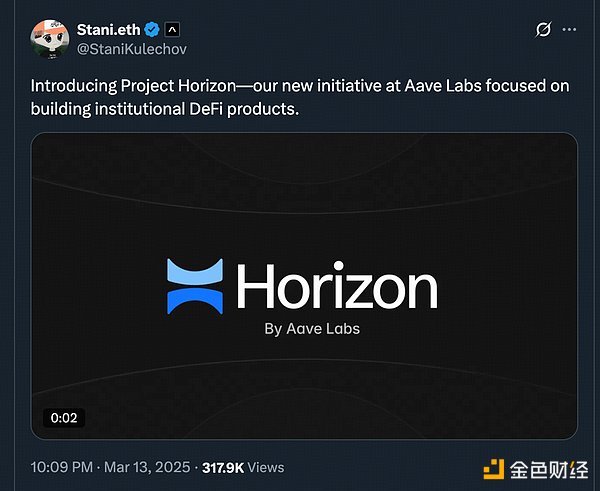
2. Uniswap and Aave are the first to have institutional-level integration capabilities: With V4's "hooks" modular architecture to support compliance functions such as real-time KYC/AML, whitelist pools, etc., Uniswap can serve as a backend DEX service for brokers and become the on-chain liquidity core for RWA (real world asset) transactions. Aave actively expands the institutional market through permissioned lending pools, RWA-collateralized lending models, and cooperation with new banks. The Horizon project is committed to building DeFi products for traditional capital markets.
3. MakerDAO faces stablecoin regulatory challenges and is actively seeking solutions: MakerDAO, which has been renamed Sky, may have conflicts with the GENIUS Act in terms of 1:1 reserves, licensed issuance, KYC, and other aspects of its DAI/USDS model. Possible response strategies include increasing the reserve ratio of traditional assets and launching compliantly designed stablecoins (with regulatory-friendly mechanisms such as freezing functions) to maintain the development space of stablecoin business in the new environment.
Introduction: "DeFi and the American Spirit"
US cryptocurrency regulation is undergoing a fundamental shift. In June 2025, Paul S. Atkins, the new chairman of the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, delivered a landmark speech entitled "DeFi and the American Spirit." In stark contrast to the previous administration’s approach, Atkins explicitly supports the core principles of decentralized finance (DeFi), arguing that it is consistent with American values.
The key policy signals sent by this speech and related developments include:
1. Protecting self-custody rights, confirming the ability of individuals to hold cryptocurrencies in personal wallets without mandatory intermediaries.
2. Recognizing that proof of stake is not a securities activity, reversing previous enforcement actions against the proof of stake mechanism.
3. Developer and open source protection, pointing out that writing or publishing decentralized code alone does not trigger securities or broker-dealer liability.
4. Turning to formal rulemaking, replacing “enforcement regulation” with transparent public guidance and rules.
5. Consider an “innovation exemption” to provide DeFi projects with temporary, conditional exemptions to operate within specified parameters, encouraging responsible experimentation while the regulatory framework is finalized.
These changes not only signal regulatory clarity, but also a possible bridge between decentralized innovation and the traditional financial system. For the top DeFi protocols, this new environment presents a rare opportunity: they have the opportunity to integrate with traditional financial infrastructure, work with regulated institutions, and expand their utility beyond the native world of cryptocurrency.
Strategic Positioning of Top DeFi Protocols
The following table assesses how the major DeFi protocols could benefit from a more favorable U.S. regulatory environment. The “Path to Traditional Finance Integration” highlights how these protocols fit into regulated financial infrastructure.
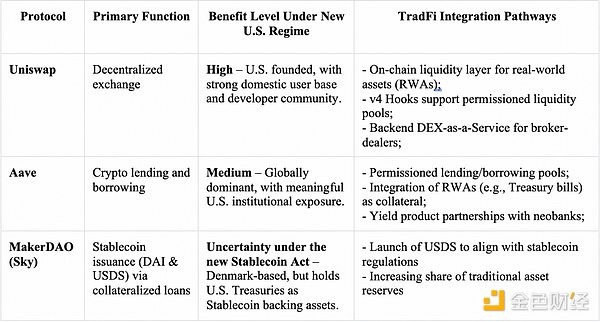
Uniswap: DEX pioneer, ready to go
As the leading decentralized exchange (DEX), Uniswap enables peer-to-peer token swaps through automated market maker smart contracts. Currently, it holds about $4 billion to $5 billion in liquidity on Ethereum and multiple other chains. Uniswap's first-mover advantage and continuous product innovation (especially in versions V3 and V4) have enabled it to maintain strong user market share, network penetration, and high protocol transaction volume despite intensified competition and enhanced incentive mechanisms.
Uniswap was created in November 2018 by Hayden Adams, a former mechanical engineer at Siemens, and developed by Uniswap Labs, a software company based in Brooklyn, New York, USA.
Main Benefits
Uniswap pioneered the concept of automated market makers (AMMs), fundamentally reshaping on-chain trading by eliminating the need for traditional order books. Uniswap v3 made a breakthrough in centralized liquidity, allowing liquidity providers to more efficiently allocate funds within a custom price range, significantly improving capital efficiency and reducing slippage. Uniswap v4 brings a new architectural leap, introducing "hooks" - a customizable smart contract that enables developers to build new features such as dynamic fees, on-chain price limit orders, and composable strategies.
Uniswap has achieved extensive multi-chain layout and can run on mainstream blockchains such as Ethereum, Polygon, Arbitrum, Optimism, Base, etc. Uniswap recently launched Unichain, a dedicated Layer 2 network built on OP Stack, which aims to provide Uniswap with native scalability and achieve faster and lower-cost DeFi settlement while maintaining deep integration with the Ethereum ecosystem.
The protocol benefits from a strong governance system supported by the UNI token. The Uniswap DAO plays an important role in funding ecosystem development, managing protocol upgrades, and allocating resources such as the Uniswap Grant Program.
Integration with TradFi as an on-chain liquidity layer
With increasing regulatory clarity and support for innovation-friendly DeFi frameworks, Uniswap is ready to bridge the gap with traditional finance. As institutions increasingly tokenize real-world assets (RWAs) such as U.S. Treasuries, equities, and private credit, Uniswap can serve as a core on-chain liquidity layer, providing 24/7 trading, deep composability, and automated market making through its mature AMM model.
Uniswap v4 further enhances this potential through its modular hook architecture, enabling on-chain compliance capabilities through the following hooks:
1. Real-time KYC/AML verification
2. Transaction monitoring
3. Wallet address whitelisting
These tools allow the creation of permissioned or compliant liquidity pools, promoting institutional participation without compromising protocol neutrality.
In addition, Uniswap can be embedded into broker-dealer platforms as a backend DEX-as-a-service provider, leveraging smart order routing and APIs to provide regulated firms with real-time price discovery and liquidity for tokenized assets. This integration model positions Uniswap as a foundational protocol for DeFi and a compliant infrastructure layer for the evolving tokenized financial system.
Aave: Lending Protocols Are Ready for the Big Scene
Aave is a decentralized money market protocol for lending and borrowing cryptocurrencies. It is one of the giants in the DeFi space, with a total locked value (TVL) of about $24 billion, making it the largest DeFi protocol by this measure. Aave allows users to earn interest on deposits and borrow assets against collateral through smart contracts. It has a global user base and actively works with institutions (for example, Horizon, a new project aimed at attracting more institutions to use Aave).
Main advantages
Since its launch, Aave has earned a good reputation as a pioneer in the lending space, supporting a variety of crypto assets on major blockchains such as Ethereum, Avalanche, Polygon, etc.
Aave adopts a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) model, and AAVE token holders can propose and vote on topics such as protocol upgrades, new asset listings, incentive plans, and risk adjustments. This open governance structure is conducive to promoting community participation, iterative development, and protocol resilience. It is worth mentioning that key decisions such as the release of Aave V3 and the expansion of new chains are determined by community consensus.
Safety is a cornerstone of Aave’s design. Its conservative risk management practices, especially around asset onboarding and liquidity parameters, have helped the platform avoid major vulnerabilities while operating at scale.
Integration with TradFi
Aave can integrate with traditional finance through several strategic avenues that align with regulatory requirements and institutional needs.
One of the most direct avenues is a permissioned version of the protocol built specifically for institutions. This framework allows regulated financial entities such as banks, asset managers, and fintechs to participate in decentralized lending in a whitelisted environment that complies with KYC/AML requirements.
Another avenue is the adoption of tokenized real-world assets (RWAs) on Aave. By allowing tokenized government bonds, real estate, or invoices to be used as collateral, Aave can attract traditional capital market participants. These assets will enable more common use cases, such as borrowing against Treasuries, or providing liquidity for yield products similar to fixed-income instruments.
Specifically, Aave developed Horizon with the goal of developing products for institutional adoption. Its first product will be a structured real-world asset solution that allows institutions to use tokenized money market funds as collateral to access stablecoin liquidity - with Aave's stablecoin GHO serving as the primary source of liquidity.
Aave can also establish partnerships with new banks and fintech companies to integrate DeFi yield strategies into consumer-oriented platforms. In this model, users deposit fiat currency, which is converted into stablecoins and loaned out on Aave. The interest generated is then returned to the user, and the entire process is completed in a seamless and familiar interface, hiding the complexity of cryptocurrency interactions.
MakerDAO (Sky): Navigating New Stablecoin Regulations
MakerDAO, recently rebranded as Sky, operates the largest decentralized stablecoin, DAI (and Sky’s reformed USDS). Historically, DAI’s crypto-collateralized model has allowed it to thrive outside of traditional banking regulation. As U.S. lawmakers advance the GENIUS Act, MakerDAO finds itself at a crossroads: whether to benefit from broader stablecoin adoption or navigate new regulatory hurdles.
Overview of the Key Provisions of the GENIUS Act
1. 1:1 Reserve Backing: Stablecoin issuers must fully back their tokens with high-quality liquid assets on a one-to-one basis (e.g., every $1 of stablecoin = $1 of USD cash or U.S. Treasury assets).
2. Licensing and Regulation: Only "approved stablecoins" - that is, entities licensed at the state or federal level - can issue payment stablecoins in the United States. Large issuers (market capitalization of more than $10 billion) will be directly subject to federal regulation (Federal Reserve/Office of the Comptroller of the Currency), while smaller issuers can choose to be regulated at the state level if they meet equivalent standards.
3. KYC/AML Compliance: All stablecoin issuers will be treated as regulated financial institutions under the Bank Secrecy Act. They must implement "KYC", anti-money laundering programs, and sanctions screening like banks.
Conflict with MakerDAO’s decentralized model
MakerDAO’s DAI/USDS stablecoin design conflicts with several core requirements of the GENIUS Act:
1. Crypto Collateral vs. Fiat Reserves: DAI is primarily backed by crypto assets such as ETH and tokenized real-world assets, rather than holding an equivalent of $1 in cash for each DAI. As of mid-2025, only 10% of DAI’s collateral is US Treasuries, the vast majority of which comes from crypto loans.
2. No Legal Issuer or License: DAI is issued by autonomous smart contracts, not companies. No registered company can currently obtain a license or audit from a regulator to become a “DAI Issuer.” However, the GENIUS Act limits the issuance of stablecoins to regulated, licensed entities.
3. KYC Controls:MakerDAO is an open protocol: anyone with crypto can open a vault and generate DAI or make permissionless transactions. No identity verification or on-chain transaction monitoring is required.
MakerDAO’s Potential Adaptability
Recognizing these risks, the MakerDAO community (led by founder Rune Christensen’s Endgame Initiative) is considering several strategies to survive and thrive under the new regulations:
One immediate response is to hold more traditional assets to back DAI, bringing it closer to the 1:1 reserve ideal. In fact, MakerDAO has already begun this transition - currently, more than $1 billion of DAI is backed by real-world assets such as short-term U.S. Treasuries and bank deposits. Maker could take this a step further by allocating a larger portion of collateral to stable, low-risk instruments (even if not abandoning crypto collateral entirely).
Another tweak would be to create a compatible wrapper or parallel stablecoin that interfaces with the U.S. market. MakerDAO’s rebrand to Sky and the launch of USDS appear to be a step in this direction. The new USDS stablecoin is designed with regulatory compliance features, including an upgradeable freeze function that can lock tokens as required by law.
 Weatherly
Weatherly






