Written by: Yashas NaikCompiled by: Block unicorn
Foreword
Ethereum faces major challenges in 2025:
Its price has not reached a new high
The ETH/BTC trading pair has fallen to a five-year low (0.02)
Competing narratives such as L2 and re-staking have failed to enhance its value.
At the same time, transaction fees have fallen to their lowest level since 2020, averaging only $0.36 per transaction.
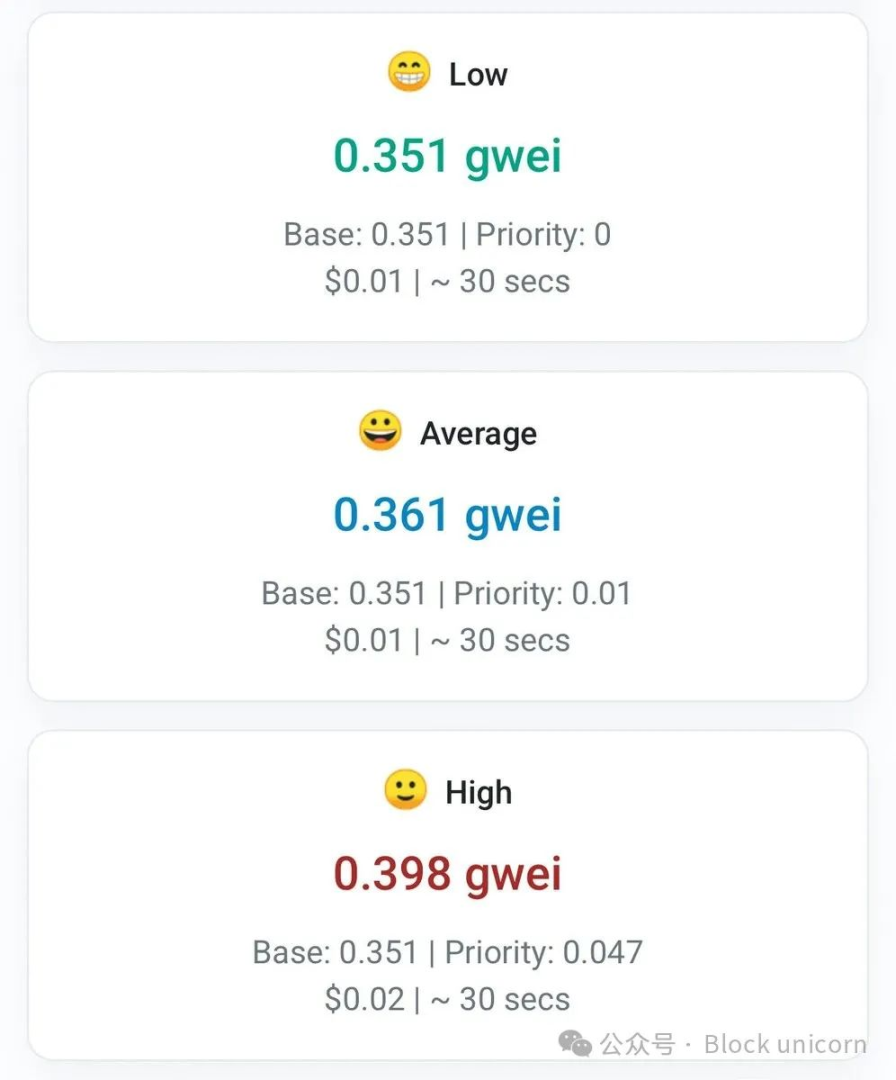
In comparison, Solana has 3.25 million daily active users (Ethereum is 410,000) and a daily transaction volume of 35.99 million (Ethereum is 1.13 million). Many people are beginning to wonder what the future direction of this second largest blockchain will be?
Two major developments may reshape the future of Ethereum:
Pectra upgrade (launched on May 7, 2025)
The Pectra upgrade combines two separate updates (Prague at the execution layer and Electra at the consensus layer) into a comprehensive improvement. Containing 11 EIPs, Pectra aims to improve scalability, efficiency and security.
Key improvements of Pectra
1. Stronger scalability
PeerDAS and Verkle Trees technology will improve transaction processing capabilities
Optimized data storage will reduce node operating costs
Hash tree technology will speed up network synchronization
2. Lower transaction costs
Reducing network congestion will significantly reduce gas fees
EIP-7702 enables account abstraction, allowing users to use stablecoins instead of ETH pays gas fees
Batch transactions and customized security features will improve wallet functionality
3. Enhanced Staking
EIP-7251 increases the maximum stake per validator from 32 ETH to 2048 ETH
This improvement reduces operating costs for large participants while retaining penalties for violations
EIP-6110 moves validator deposit processing to the execution layer, reducing validator activation time by approximately 48 hours
RISC-V Proposal (Long-term Solution? )
V God recently proposed replacing the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) with RISC-V technology. This change will fundamentally change the way Ethereum executes smart contracts.
What is RISC-V?
RISC-V is an open source instruction set architecture. (Essentially a computer language that tells a processor how to execute commands)
Unlike the EVM designed specifically for Ethereum, RISC-V is:
Open source and free to use
Already widely adopted in the computing field
Processes complex calculations more efficiently
Better suited for zero-knowledge proof technology
Why replace EVM?
1. Performance improvement
Complex operations such as privacy transactions and cross-chain functions will become more practical
2. Zero-knowledge proof compatibility
The current zkEVM system must convert EVM instructions to RISC-V to generate proofs
This conversion will incur 100 to 1000 times the computational overhead
Native RISC-V support will eliminate this conversion step
zkVMs like @SuccinctLabs SP1 can run smart contracts directly
3. Developer Continuity

3. Developer Continuity
The Pectra upgrade addresses pressing issues in staking, transaction costs, and user experience. The RISC-V proposal addresses Ethereum's basic execution architecture, which could lay the technical foundation for it to compete with faster blockchains while maintaining its security and decentralization advantages.
For users, these changes ultimately mean:
Faster transaction processing
Lower fees
New application possibilities (e.g. on-chain AI, privacy features)
Better scalability without sacrificing security
By retaining compatibility with existing applications while planning for better performance improvements, Ethereum is attempting to evolve without abandoning its core principles or ecosystem. Whether these changes will be enough to maintain its market position and fend off fast-growing competitors remains to be seen.
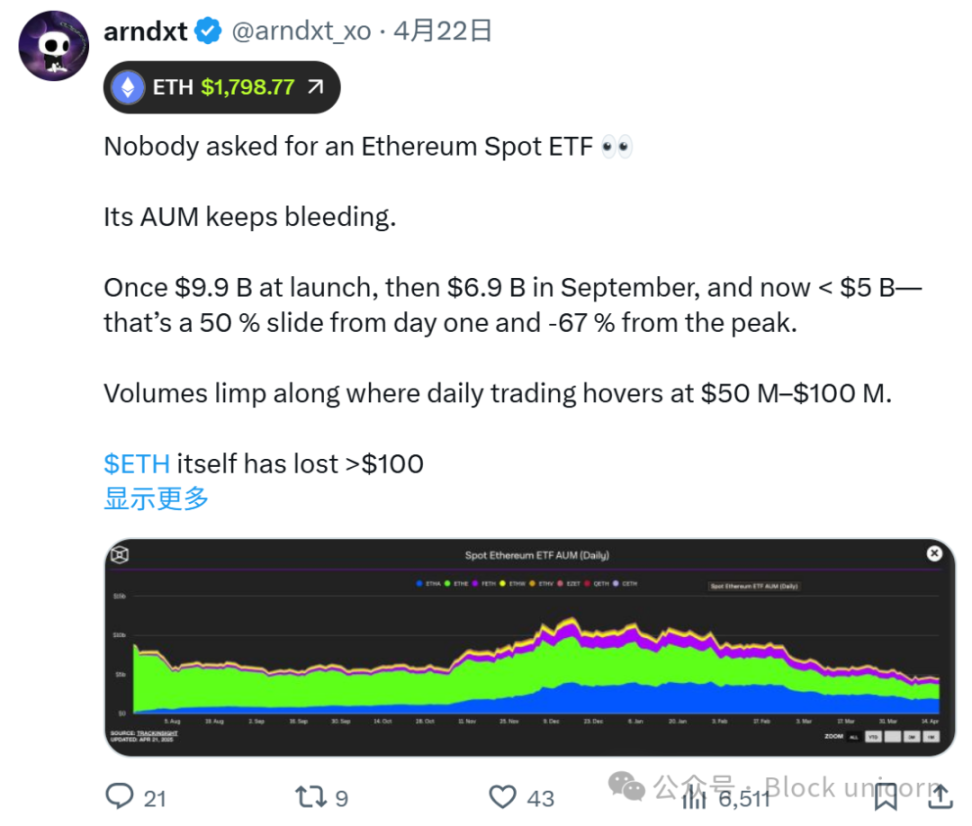
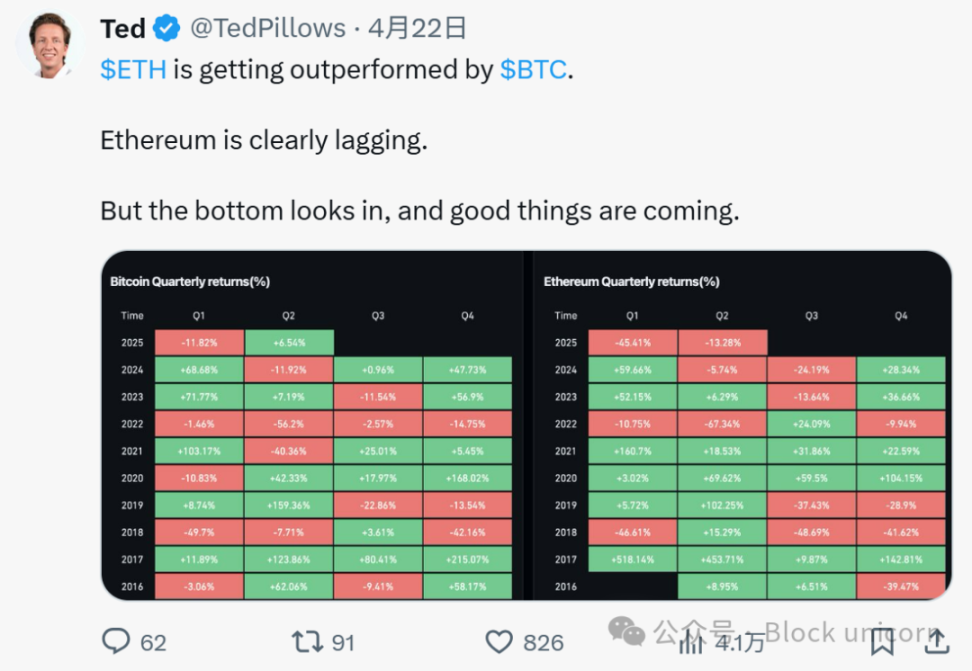
If not Ethereum, then who?
Recent data shows a significant shift in the competitive landscape. While the top ten DeFi protocols still run on Ethereum, we’re already seeing warning signs that its dominance is fading.
Projects like Jito and Jupiter are gaining traction in other areas, while Converge (Ethena’s RWA chain) has exited the ecosystem entirely. These changes suggest that Ethereum’s lead is not secure, which raises an important question:
What new technological breakthroughs does Ethereum need to remain competitive in the future?
According to Nansen, Solana recently surpassed Ethereum in total staked market capitalization (an important milestone for the SOL ecosystem), showing growing institutional confidence in Solana’s staking infrastructure.
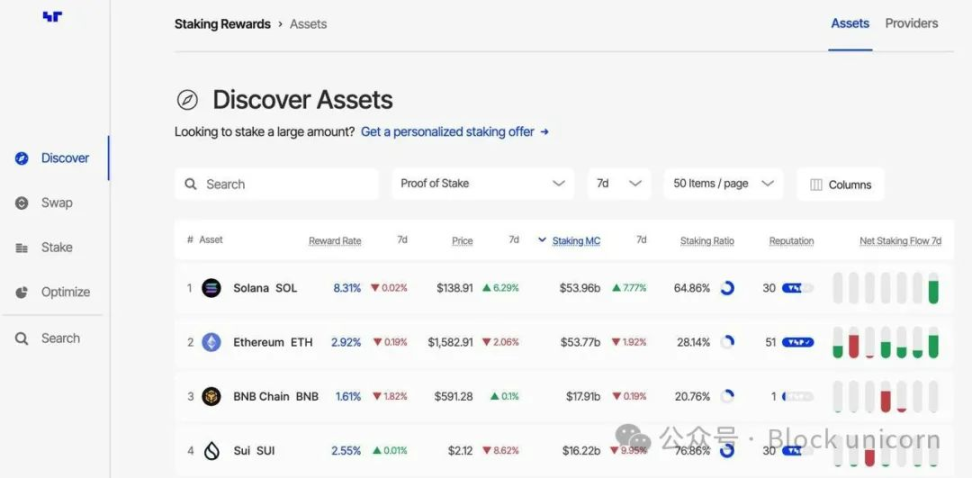
Meanwhile, Solana’s revenue performance in the first quarter of 2025 outperformed all other chains while maintaining extremely low transaction fees. The combination of high revenue and low user costs demonstrates Solana’s efficient economic model.
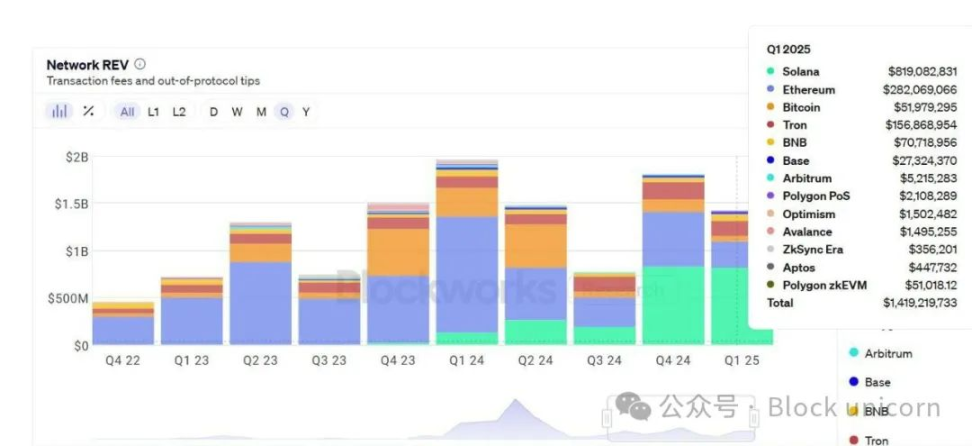
These developments add additional pressure to Ethereum’s technical roadmap. As Pectra and a potential RISC-V transition aim to address Ethereum’s scalability and cost issues, Solana continues to gain traction with its existing architecture.
 Anais
Anais









