Author: 0xyanshu Source: Shoal Research Translation: Shan Ouba, Golden Finance
Introduction
Blockchain networks have undergone significant architectural advancements to address scalability challenges. Solana stands out as a high-performance blockchain that optimizes scalability and throughput with its unique execution architecture. Unlike traditional blockchain designs that rely on sequential processing, Solana introduces a parallel execution model supported by the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM). As an execution environment for smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps), SVM enables Solana to handle more transactions per second (TPS) than other blockchain architectures.
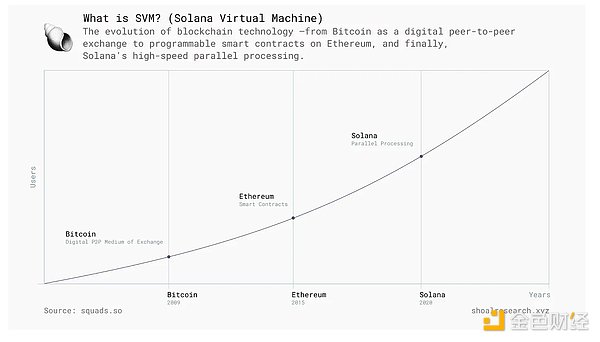
To further expand the capabilities of SVM beyond Solana, SOON Network has launched a second layer (L2) network based on SVM, settled on Ethereum while retaining Solana's execution advantages. SOON achieves cross-chain interoperability, reduces transaction costs, and improves developer experience by extending SVM to major Layer 1 networks.
This report will provide an overview of SOON’s architecture, ecosystem, and growth strategy, delve into the advantages of SVM over EVM, the technological advancements behind SOON, and the SOON Big Bang Plan - a long-term incentive program to drive ecosystem development, covering partnership integration and NFT empowerment.
Solana’s Modular Approach and Solana Virtual Machine (SVM)
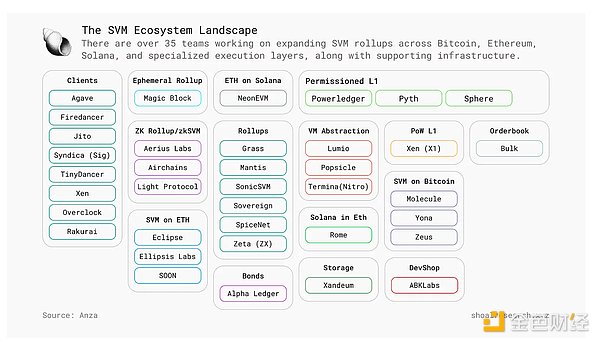
The recent shift in blockchain architecture toward modular design has further enhanced Solana’s capabilities. Previously, the Solana validator client was tightly integrated with the SVM, which limited innovation and required adjustments at the system level for any changes. However, in July 2024, Anza launched the SVM API, marking a major change to Solana’s execution environment, allowing developers to decouple the SVM from the validator client (Agave). Based on this breakthrough, SOON became the first protocol to utilize a decoupled SVM, extending Solana’s execution capabilities beyond its native ecosystem and driving wider adoption of SVM Rollups. This modular design enables developers to independently optimize the execution environment without impacting consensus, the network, or block production mechanisms. A growing number of projects are innovating with this flexibility, including: • Permissioned L1 Networks: A compliance architecture similar to SWIFT while automating manual processes (such as Sphere).
• Decentralized Storage Solutions: Expand Solana’s program capacity (e.g. Xandeum).
• EVM and Solana Interoperability: Run Ethereum on Solana, Solana on EVM, and native Solana Rollup (e.g. Ellipsis, Neon, Soon).
• Bitcoin x Solana Cross-Chain: Combine with new cross-chain applications (e.g. Yona, Molocule, Zeus).
• Next-generation validator clients: Such as the Firedancer launched by Jump, demonstrated at the Breakpoint conference, with a theoretical maximum throughput of 1,000,000 TPS.
• zkSVM, Rollup, AI combined with blockchain and other cutting-edge innovations.
Solana’s Modularity Report (by Delphi) points out the key advantages of this approach, including:
• Independent Innovation: Developers can iterate on the SVM without modifying the validator client.
• Optimized Performance: The execution environment can be customized to suit specific needs.
• Diverse implementations: Multiple SVM variants can be created, suitable for DeFi, games, and AI dApps.
• Interoperability standards: The rise of multiple SVM versions has led to the birth of new cross-chain standards.
• Improved developer experience: Decoupling the execution layer from the consensus layer simplifies smart contract development and deployment.
SVM vs. EVM: Architecture and Performance Differences
Although the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM) and the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) are both execution environments for smart contracts, there are fundamental differences between the two in terms of architectural design and transaction processing.
1. Execution Model
The EVM runs in a single-threaded environment, processing transactions sequentially. While this ensures security and consistency, it can lead to bottlenecks when transaction volumes are high, causing network congestion and increased gas fees. The SVM employs parallel execution through its Sealevel engine, allowing multiple non-conflicting transactions to run simultaneously on different cores of the validator hardware. This multi-threaded approach enhances scalability and reduces latency, enabling Solana to achieve significantly higher throughput at a lower cost.
2. State and Data Management
Ethereum’s account model stores balances and state in a single smart contract. When multiple contracts attempt to read or modify the same account data at the same time, potential conflicts arise.
In contrast, Solana’s explicit state access model requires transactions to specify the account to interact with before execution. This design eliminates runtime conflicts and allows independent transactions to be processed simultaneously.
3. Hardware Utilization
Due to the single-threaded nature of the EVM, it cannot fully utilize modern multi-core processors, resulting in insufficient utilization of validator hardware. SVM is designed to effectively utilize multi-core processing power, distribute transaction execution across multiple threads, and ensure optimal hardware scaling.
4. Fee Market Design
Ethereum uses a global fee market, and a surge in demand in one area (such as NFT minting) can cause a surge in gas fees across the entire network, affecting unrelated transactions. This can result in high and unpredictable costs for users.
Solana leverages Sealevel's parallel processing capabilities to implement a localized fee market. Each smart contract operates independently in fee calculation, preventing congestion in one area from affecting the entire network. This ensures lower and more predictable fees.
SOON Network: Scaling Solution Based on SVM L2
SOON (Solana Optimistic Network) is a high-performance SVM Rollup that aims to promote the large-scale application of blockchain technology by extending Solana's execution environment to major Layer 1 (L1) networks. Unlike traditional Ethereum Rollup, SOON uses a decoupled Solana virtual machine (Decoupled SVM) to optimize execution speed and scalability. Its core technology is based on SOON Stack, a modular Rollup framework that allows SVM-compatible Layer 2 (L2) networks to be deployed on any L1.
SOON’s architecture consists of three core components:
• SOON Mainnet - a general-purpose SVM L2 for settlement on Ethereum.
• SOON Stack - a modular Rollup framework that supports the creation of SVM-based Rollups on different L1s.
• InterSOON - a cross-chain messaging protocol that enables seamless interoperability between SOON and other blockchain networks.
In the following sections, we will explore how SOON combines high-performance execution, cross-chain interoperability, and scalability to build a unified blockchain ecosystem and break down barriers between different chains.
SOON's core philosophy revolves around the Super Adoption Stack (SAS), with the goal of creating a fully interoperable blockchain future where all networks can communicate seamlessly. The two key pillars of SAS are:
1. High-performance execution - Introducing SVM into mainstream L1 ecosystems (such as Ethereum, Bitcoin, BNB, TON) to improve execution efficiency.
2. Seamless interoperability - Establish cross-chain communication between SVM L2s and all major L1s to achieve smooth asset transfers and dApp interactions.
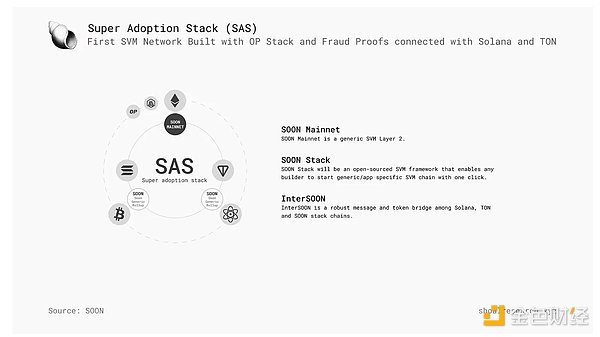
SOON Mainnet and SOON Stack are the core components to realize this vision, enabling developers to deploy SVM Rollup on different L1s while ensuring the smoothness of cross-chain connections through InterSOON.
SOON Mainnet: The First Decoupled SVM Rollup
SOON Mainnet is an L2 solution settled on Ethereum and uses decoupled SVM as the execution layer. Unlike traditional EVM Rollup, SOON Mainnet adopts SVM, which has unparalleled advantages in speed, scalability and efficiency:
• SVM-driven execution - faster and more efficient than traditional EVM Rollup.
• Interoperability with Ethereum - supports native ERC-20 <> SPL asset cross-chain for seamless transfers.
Security is an important difference between SOON and other SVM Rollup projects. According to L2Beat data, SOON is a Rollup, not a sidechain. Unlike Rollup, sidechains need to build their own security mechanisms and validator nodes, which may not be as secure as the main chain in the early stages.
SOON adopts the Rollup mechanism to ensure that when the Sequencer fails, users can still submit transactions directly to L1, thereby ensuring the accessibility and security of on-chain operations.
Many SVM Rollups only replicate Solana's execution model without providing additional security guarantees. SOON enhances security through Merklization and State Root Verification, which are similar to account snapshots of blockchains and are permanently stored on Ethereum.
In simple terms, Merklization is how SOON structures blockchain data into a Merkle tree, allowing transactions and balances to be verified efficiently and securely. It ensures anti-fraud security, greater scalability, and trustless withdrawals between Layer 2 and Layer 1.
This allows users to mathematically verify their funds at any time, eliminating the need to rely on a trust-based security model.
Permanent and verifiable access to transaction history, unlike other SVM projects that impose a 150-slot limit.
Fund verification based on mathematical proofs rather than relying on aggregated internal data.
Independent transaction verification through Merkle proofs ensures that users can verify their own balances without exposing others’ data.
SOON’s Core Technical Innovation
Decoupled SVM – SOON separates SVM execution from Solana’s native consensus, allowing SVM to be used as an independent execution layer for aggregation.
Merklization – Use Merkle Patricia Trees (MPT) to efficiently verify state transitions, consistent with Ethereum’s proof verification model for seamless integration.
Horizontal Scaling - Unlimited scalability by adding more validator nodes, ensuring high throughput and reliability without overloading a single machine.
By combining the security and liquidity of Ethereum with the high-performance execution of Solana, SOON Mainnet provides a next-generation Layer 2 experience for Solana and Ethereum developers. SOON’s public mainnet recently went live, with more than 20 ecosystem projects deployed, including Ethereum’s official SOON Native Bridge and Solana and TON’s InterSOON. With the first round of NFT minting raising $22 million, details about the second round of COMMing SOON NFT will be announced soon, providing new benefits for early participants (we will cover COMMing SOON NFT and SOON Big Bang in detail)
SOON Stack: Modular SVM Rollup Framework
SOON Stack is a flexible rollup infrastructure that allows developers to deploy SVM-based rollups on different L1s. Chains built with SOON Stack are called SOON Chains, and they retain the advantages of SOON's decoupled SVM and the parallel execution capabilities of SVM while maintaining compatibility with Ethereum's OP Stack.
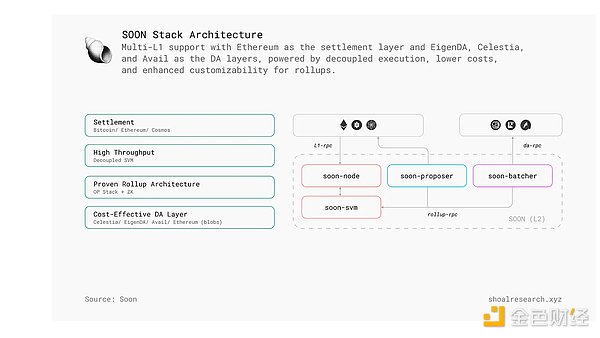
Main Features of SOON Stack
Multi-L1 Support - Supports Ethereum as the settlement layer and integrates EigenDA, Celestia and Avail for data availability.
Performance Optimization – Using a decoupled SVM, execution is separated from Solana’s consensus, reducing unnecessary data availability costs.
Customizable Rollups – Enables builders to launch SVM Rollups with fine-tuned parameters for DeFi, gaming, and other applications.
Use Cases for SOON Stack
AI and DePIN – SOON Stack provides high-performance execution for DePIN and AI-driven applications. For example, SOON recently partnered with IoTeX to enable real-time data processing, device-to-blockchain interaction, and large-scale AI automation. DePIN networks need to provide fast and cost-effective transaction processing for IoT devices, sensors, and machine learning models, while AI-driven dApps require low-latency inference and secure data exchange - SOON achieves both through decoupled SVM and parallel transaction execution.
Financial and DeFi protocols - Optimized for high-volume transactions with low latency.
Custom Gas Fee Model - Applications can implement a customized Gas structure, improving the user experience (UX).
SOON Stack Adoption and Growth
SOON Stack has partnered with Cytonic, CARV, and Lucent Network, marking an important step in expanding the SVM-based rollup ecosystem. These projects leverage SOON’s Decoupled SVM architecture to build scalable, high-performance blockchains:
Cytonic has pioneered multi-VM interoperability, enabling dApps from Solana, Ethereum, and other blockchains to coexist seamlessly. Cytonic is building its first SVM-based chain with Caldera and SOON Stack.
SOON is powering CARV’s SVM chain with SOON Stack. CARV is building an AI-driven data economy chain, integrating a trusted execution environment (TEE) and zk-proofs for privacy and security.
Lucent Network (formerly Clover) is introducing an AI-optimized financial and SocialFi ecosystem and will use SOON Stack to build an SVM-based AI-driven network.
In addition, SOON has partnered with Caldera, the fastest-growing Rollups as a Service (RaaS) provider, to support SVM-based Rollups. The collaboration makes it easier for projects to launch application-specific SVM chains with one-click deployment and modular execution.
By providing a standardized SVM rollup framework, SOON Stack enables developers to build and scale high-performance Layer 2 chains, thereby promoting the development of next-generation AI, DePIN, and decentralized financial solutions without the limitations of EVM.
InterSOON: Enabling Seamless Cross-Chain Communication
InterSOON is a cross-chain messaging protocol that enables smooth interaction between SOON Mainnet, SOON Stack, and other L1s. Unlike traditional token bridges that cause liquidity fragmentation, InterSOON allows smart contracts and assets to interact natively across multiple chains.
Key Features of InterSOON
Unified Message Standards – Eliminates the need for custom bridges by enabling standardized communications.
Preserves Liquidity – Avoids liquidity fragmentation by maintaining assets in their native form.
Improved Performance – Decoupled SVM optimizes cross-chain interactions by eliminating unnecessary bridging overhead.
By using Hyperlane as its messaging backbone, InterSOON provides a scalable and trustless communication layer for the next generation of multi-chain applications.
Community Fundraising Launch Mechanism: A New Model for Value Distribution
A major challenge facing token issuance today is the lack of accessibility, fairness, and coordination between projects and communities. Existing distribution models tend to favor venture capitalists (VCs) and early insiders, while excluding users who contribute to network growth. This disconnect leads to long-term poor coordination, speculative cycles, and reduced community engagement.
Issuances based on community NFT minting (such as SOON’s recently launched COMMing SOON NFT round, which we will discuss in more detail in a later section) provide a permissionless, transparent, and incentive-driven mechanism for communities to raise funds while ensuring that value is distributed to investors. This approach integrates customizable pricing, flexible vesting, and NFT-bound token rights to create a sustainable and decentralized token issuance framework.
How Community NFT Mint Achieves Fair and Efficient Fundraising
Unlike traditional token issuance that prioritizes exclusive allocations, the community NFT minting model provides a transparent and adaptable mechanism for raising funds while ensuring that community participants receive long-term incentives and governance influence.
1. Tokenized participation through NFT
Participants do not sell tokens directly, but mint NFTs that contain token rights, vesting conditions, and additional benefits.
These NFTs represent customized token access, allowing users to choose terms based on their risk preferences.
Investors can trade these NFTs, providing a liquid market for vested token rights before the actual tokens are unlocked.
This model minimizes regulatory complexity and associated legal risks.
2. Configurable Pricing and Vesting Structure
The multi-tier pricing model enables users to choose to obtain immediate liquidity at a higher price or obtain longer vesting at a discounted price.
This eliminates the forced price distortion caused by fixed unlocking schedules and reduces selling pressure after launch.
Fair entry conditions ensure that both retail users and large investors have access to token supply under transparent terms.
3. Community-first fundraising model
No private rounds or backdoor deals - every allocation is open to the community.
Smart contracts manage token issuance, vesting, and allocation, ensuring trustless execution.
Eliminate pre-IPO guesswork by building a release schedule that incentivizes long-term participation rather than a quick exit.
Mechanisms for allocating value to investors
To create sustainable incentives and ensure long-term alignment with investors, the community NFT Mint model integrates multiple value return mechanisms, reducing the risks typically associated with early participation.
1. The income-generating utility of community NFTs
Projects can attach additional benefits to minted NFTs, such as:
This transforms community NFT Mint into an asset that accumulates value beyond token unlocking, thereby ensuring continued investor participation.
2. Dynamic unlocking based on network growth
Token release schedules can adapt to network adoption metrics, preventing premature liquidity events.
Community NFTs encourage investors to support ecosystem growth rather than engage in short-term speculation.
3. Embedded referral and reputation systems
Participants who drive adoption through referrals and organic contributions can receive additional token rewards.
Rank-based reward mechanisms (e.g., Kaito-style rankings) further align power users with project success.
The community NFT minting model provides a transformative fundraising approach that incorporates liquidity, flexibility, and decentralization into token issuance. By enabling NFT-bound token rights, dynamic vesting models, and ongoing value accumulation mechanisms, the system ensures long-term alignment between projects, investors, and the community.
This model is not only a fundraising mechanism, but also the foundation of a sustainable token economy that ensures projects remain decentralized, reduces early speculative risk, and promotes long-term adoption. In an industry where liquidity and consistency are critical factors for success, community NFT Mint is a scalable, inclusive, and market-responsive innovation for the next generation of Web3 projects.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
According to the latest developer report by Electric Capital, there are currently more than 24,000 monthly active developers in the blockchain ecosystem. Solana is the ecosystem that has attracted the most new developers, with more than 7,500 new developers exploring Solana and its SVM stack. This is the first time since 2016 that a blockchain ecosystem has attracted more new developers than Ethereum.
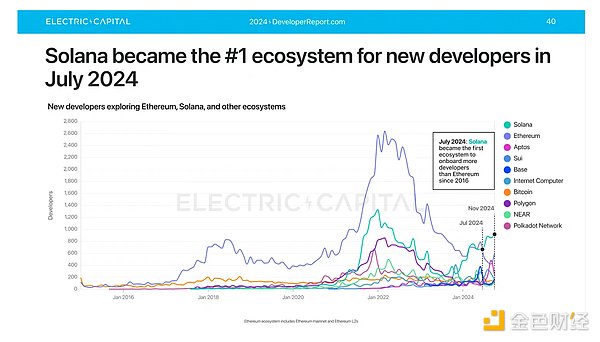
With the continuous development of the blockchain ecosystem in 2025, developers have the following three main options:
Among them, The most competitive ecosystems include Monad, Berachain, Base, MegaETH, and many emerging EVM L2 solutions. If one EVM ecosystem does not meet the needs of the team, they can easily migrate to another EVM ecosystem, leading to increased competition within the EVM ecosystem. Since the development experience of these ecosystems is roughly the same, the key factors of competition will mainly be reflected in ecosystem support, liquidity, and community strength. Although it is possible to deploy across multiple EVM ecosystems, managing multiple EVM instances will increase complexity and may affect product focus. In contrast, the SVM and Move ecosystems have higher developer retention and talent density because there are fewer competitive platforms to choose from. This means that developers are more motivated to stay in the same ecosystem, accumulate deeper expertise, and promote ecological innovation.
Although EVM is the most mature ecosystem at present, it has fewer opportunities for innovation and its progress is relatively slow. In contrast, SVM and Move ecosystems will have a technological lead in 2025, and with less competition and a higher concentration of talent, developers can get stronger incentives and promote faster technological evolution.
But their long-term success depends on one core factor:
How quickly can SVM and Move ecosystems improve the developer experience, including contract layer optimization, data reading improvements, and core protocol optimization.
Solana's development experience has improved by 2-5 times, and the ecosystem has grown by 10 times?
As 0xMert_, co-founder of Helios Labs, said:
If Solana can improve the developer experience by 2-5 times by 2025, its growth rate may be 10 times that of other ecosystems.
Currently, the SVM ecosystem has: 500+ full-time developers,more than 3.3K monthly active developers,54K+ code bases,more than 15 million code commits.
As the number of developers continues to grow, the SVM ecosystem is gradually becoming a core participant in blockchain innovation. This trend shows that the market demand for SVM is increasing, and the potential value of SVM as a high-performance, scalable architecture is rising.
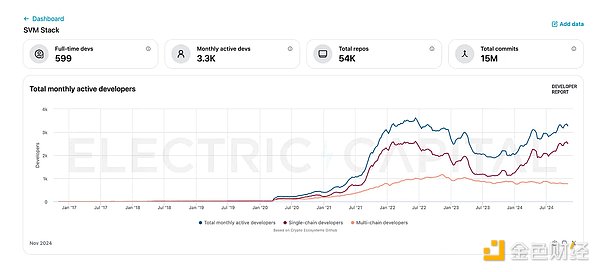
Under this trend, SOON Network provides developers, users and enterprises with a strong competitive advantage in 2025, especially projects that want to deploy application-specific chains (Appchains).
Appchains are becoming the best choice for enterprise applications (especially in finance and gaming) because they have:
High performance, seamless experience and enhanced security
Lower cost, customization and experimental space
Greater flexibility in governance, consensus mechanism and economic model
Unlike general-purpose L2, Appchains relies on L1 to provide security and network operation, avoiding competition with other applications for storage and computing resources. This means that developers can gain greater value while maintaining control over the execution environment.
As the demand for scalable, application-specific Appchains rises, SOON Network is at the forefront of Modular Execution, enabling Solana’s SVM as a dedicated execution layer across multiple L1s.
As the demand for scalable, application-specific chains grows, projects like SOON Network are at the forefront of Modular Execution, enabling Solana’s SVM as a dedicated execution layer across multiple L1s.
By leveraging decoupled SVMs, Merklization, and horizontal scaling, SOON enhances scalability, efficiency, and interoperability. As SVM adoption continues to increase, SOON’s modular framework positions itself as a key player in blockchain scaling, combining Solana’s speed with Ethereum’s security and fostering a more connected, efficient multi-chain ecosystem.
In addition, the InterSOON messaging infrastructure enhances interoperability and composability between application chains, thereby strengthening the SVM stack as a viable framework for next-generation blockchain expansion.
 Brian
Brian










