Written by: AIMan@黄金财经
As the saying goes, there is pressure only when there is competition. After the US Senate accelerated the legislative process of the stablecoin GENIUS Act, the Hong Kong Stablecoin Regulatory Act was passed ahead of the United States.
On May 21, 2025, the Hong Kong Legislative Council officially passed the Stablecoin Bill at the third reading. The bill will officially come into effect as long as the Chief Executive of Hong Kong signs it and publishes it in the Gazette. This means that Hong Kong will officially implement stablecoin regulation. Anyone who issues a fiat stablecoin in Hong Kong, or a fiat stablecoin that claims to be anchored to the value of the Hong Kong dollar in Hong Kong or abroad, must apply for a license from the Hong Kong Monetary Authority.
This article briefly reviews the important process and main contents of the Hong Kong "Stablecoin Bill".
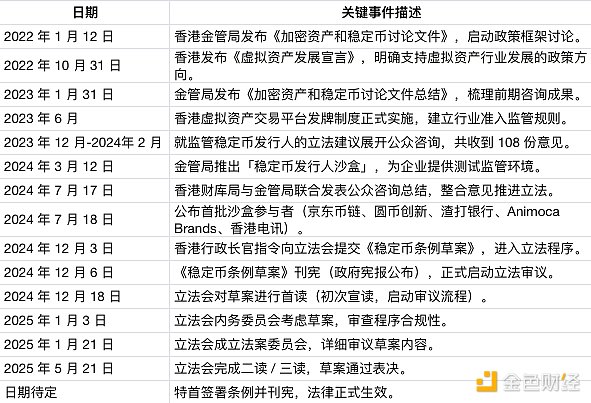
Important History of the Stablecoin Bill
On January 12, 2022, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority released a discussion paper on crypto assets and stablecoins
On October 31, 2022, the Hong Kong Virtual Asset Development Declaration
On January 31, 2023, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority released a summary of the discussion paper on crypto assets and stablecoins
In June 2023, the licensing system for virtual asset trading platforms in Hong Kong was implemented
From December 2023 to February 2024, a public consultation document was released Collecting opinions on legislative proposals on regulating stablecoin issuers, a total of 108 opinions were received
On March 12, 2024, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority launched the Stablecoin Issuer Sandbox
On July 17, 2024, the Hong Kong Treasury Bureau and the Hong Kong Monetary Authority jointly issued a public consultation summary
On July 18, 2024, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority announced the participants of the Stablecoin Sandbox: JD CoinChain Technology (Hong Kong) Co., Ltd., Yuancoin Innovation Technology Co., Ltd., Standard Chartered Bank (Hong Kong) Co., Ltd. and Animoca Brands), Hong Kong Telecommunications
On December 3, 2024, the Chief Executive of Hong Kong instructed to submit the "Stablecoin Bill" to the Legislative Council
On December 6, 2024, the "Stablecoin Bill" was gazetted
On December 18, 2024, the Legislative Council had its first reading
On January 3, 2025, the House Committee considered
On January 21, 2025, the Bills Committee considered
On May 21, 2025, the second/third reading was passed
The date is to be determined. It will take effect after the Chief Executive signs and the law is gazetted
Main contents of the Stablecoin Bill
1. Regulatory agency
Monetary Authority
2. Regulated stablecoins
Hong Kong's stablecoin licensing system focuses on fiat stablecoins, and defines "specified stablecoins" subject to supervision by the Monetary Authority as stablecoins that claim to be anchored to one or more official currencies to maintain a stable value.
Stablecoins that refer to the value of other assets (such as commodities), in the future, the Monetary Authority may specify a digital form of value as a specified stablecoin by publishing a notice in the Gazette.
3. Regulated stablecoin activities
Any person who has not obtained a licence from the Monetary Authority shall not carry out regulated stablecoin activities in Hong Kong in the course of business, including the issuance of specified stablecoins.
Any person who actively promotes the issuance of its specified stablecoins to the Hong Kong public shall be regarded as demonstrating that it is carrying out regulated stablecoin activities and is required to obtain a licence from the Monetary Authority.
Stablecoins that are anchored to the value of the Hong Kong dollar (whether in whole or in part) should be covered as regulated stablecoin activities even if they are issued outside Hong Kong and regardless of where they are issued.
4. Licensing Criteria
Hong Kong Stablecoin Licensing Criteria include the following main elements:
(a) Management and stabilization mechanism of reserve assets:The market value of the reserve assets of the specified stablecoin must at all times be at least equal to its circulating face value. The licensee must have a robust stabilization mechanism, arrangements for properly separating and managing reserve assets, and an adequate disclosure policy;
(b) Redemption: To ensure that holders of specified stablecoins (Holders) are properly protected, the licensee must pay the face value of the specified stablecoin to the holder who makes a valid redemption request, and shall not impose overly cumbersome conditions and unreasonable fees. The redemption procedures, time limits, any conditions or fees involved and rights should also be clearly disclosed for the holder's reference;
(c) Having a physical company in Hong Kong: To ensure that the Monetary Authority can carry out effective supervision and law enforcement, the licensee must have a physical company in Hong Kong;
(d) Financial resources: The licensee must have sufficient financial resources to operate its business. 192);">including the requirement of a minimum paid-up share capital of HK$25 million;
(e) Proper Persons:The controllers, chief executive officers and directors of the licensee must be fit and proper persons, and the persons responsible for the management and operation of regulated stablecoin activities must have the necessary knowledge and experience;
(f) Prudence and Risk Management:The licensee must have appropriate risk management policies and procedures to manage the risks arising from its business operations. The relevant policies and procedures must be commensurate with the scale and complexity of its operations. The licensee should also have a sound and appropriate control system to prevent and combat possible money laundering and terrorist financing activities.
5. License Term
An open license is granted to the licensee, and the licensee's license will remain valid as long as it is not revoked by the Monetary Authority. The licensee will be subject to continuous supervision by the Monetary Authority.
6. Who can sell stablecoins to the public
Only the following institutions regulated by the Monetary Authority or the Securities and Futures Commission of Hong Kong can sell specified stablecoins to the public:
(a) licensees under the fiat stablecoin issuer regime;
(b) virtual asset trading platforms licensed by the Securities and Futures Commission;
(c) corporations licensed by the Securities and Futures Commission to carry out Type 1 regulated activities under section 116 of the Securities and Futures Ordinance (Cap. 571);
(d) authorized institutions as defined in the Banking Ordinance (Cap. 155).
7. What are the penalties for issuing stablecoins without a licence or violating regulations with a licence?
(a) Conducting stablecoin activities without a licence: a fine of HK$5 million and seven years’ imprisonment;
(b) Selling stablecoins by non-designated licensed institutions: a fine of HK$5 million and seven years’ imprisonment;
(c) Fraudulent or deceptive conduct involving specified stablecoin transactions: a fine of HK$10 million and ten years’ imprisonment;
(d) Making fraudulent or reckless misrepresentation to induce others to obtain specified stablecoins: a fine of HK$1 million and seven years’ imprisonment.
8. What powers does the Monetary Authority have?
In order to effectively implement the system, the Hong Kong Legislative Council has given the Monetary Authority the power to carry out ongoing supervision, including requiring the submission of documents and records, issuing instructions, making regulations, issuing guidelines, etc., such as: specifying an activity as a regulated stablecoin activity; designating an entity that provides services to a stablecoin payment system as a designated stablecoin entity subject to regulatory specifications; designating a stablecoin issuer that does not need to apply for a license as a designated stablecoin entity; instructing investigators to conduct investigations, requiring the provision of evidence related to suspected violations, requiring relevant persons to assist in the investigation, and applying to a magistrate for a search warrant and seizure when necessary; and 192);">Supervisory penalties, including suspension or revocation of licences and imposition of fines not exceeding HK$10 million or three times the amount of profits gained or losses avoided as a result of the breach (whichever is higher).
 Weatherly
Weatherly



