Source: Grayscale; Compiled by: Tao Zhu, Golden Finance
Staking rewards can be a non-correlated source of income, thereby improving the total return of investing in proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain tokens.
Traditional sources of investment income, such as bond coupon payments, are closely tied to central bank policies and economic conditions. While there are ways to diversify through alternative income-generating strategies in traditional markets, most options have similar correlations to economic cycles. Staking rewards - income earned by helping to validate blockchain transactions - represent a unique potential source of income that is unrelated to the actions of the Federal Reserve or the overall economic performance.
Staking enables token holders to participate in network consensus and security and earn protocol-native rewards (i.e., income denominated in ETH or SOL rather than fiat currency). The incentives that drive staking are structurally distinct from traditional yield-earning instruments, providing a blockchain-native income mechanism within a digital asset portfolio (for more background on staking, see From Miners to Stakers: How Staking Secures the Ethereum Blockchain).
Uncorrelated Yields
Staking yields are governed by protocol-specific parameters and network layer participation rates, rather than conditions in the U.S. dollar money market. As a result, yields differ from traditional fixed income yields in terms of level and variation over time.
For example, among the top 20 proof-of-stake (PoS) digital assets, the median staking yield has consistently outperformed traditional fixed income benchmarks, such as the federal funds rate or benchmark investment-grade corporate bond yields. Since 2019, the median staking yield has fluctuated between 5% and 10% annualized (Exhibit 1).
Figure 1: Staking returns are unrelated to fixed income yields
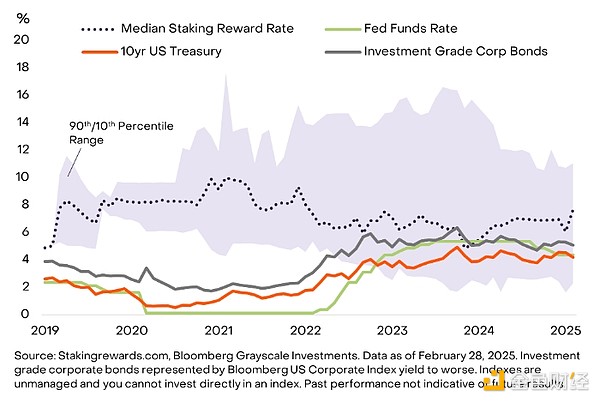
Staking rewards also show low or even negative correlation with traditional interest rate tools. In terms of monthly changes since 2019, the median staking reward in our sample has the following correlations with traditional benchmark interest rates:
-0.67 relative to the Fed Funds rate
-0.71 relative to the 10-year US Treasury yield
-0.76 relative to the US corporate bond yield
This interest rate independence increases the potential value of staking in a multi-asset portfolio, providing both the potential for income diversification and lower associated risk compared to traditional fixed income instruments.
Higher Total Returns, Equal Risk
Staking is a mechanism that can potentially increase total returns while only slightly increasing portfolio risk (through various operational risks, as described below). Staking rewards are paid in native blockchain tokens, not fiat currency. These rewards can be reinvested, compounding over time, potentially creating a dual stream of returns—capital appreciation and staking rewards—without changing an investor’s underlying exposure. In PoS networks, such returns are typically between 5%-10% per year, helping to offset volatility during market declines.
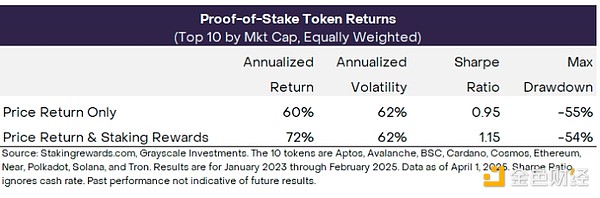
To quantify this effect, we created two hypothetical PoS token return indices: (1) an index that includes price returns only; and (2) an index that includes both price returns and staking rewards. Both indices are equally weighted and include the top 10 PoS tokens by market cap. The indices are unmanaged and you cannot invest directly in them. These results are purely hypothetical and do not reflect actual returns for investors. The underlying indices are also hypothetical and do not represent any actual indices used to evaluate broader investments. The indices were created by the authors and are constructed with the benefit of hindsight. Staking rewards are not security deposits, may not be paid, and are not an obligation of any company or government entity.
Exhibit 2 presents the return statistics for the two indices. After including staking rewards, the total return rate increases from 60% to 72%, which means the actual annual return rate is 12%. Staking rewards do not cause price volatility (although staking may bring other risks; see next paragraph), so higher returns also lead to higher Sharpe ratios.
Figure 2: Staking rewards may increase total returns
Staking rewards are generally mild relative to token price volatility, which should be considered the main risk and potential source of reward for most crypto asset investments. That being said, staking activity can also introduce new risks, including potential slashing (loss of staked assets due to failed transaction validation), lock-up periods (limited liquidity during the staking period, which may affect the portfolio's ability to rebalance and respond to market changes), and smart contract risk (the underlying staking protocol or smart contracts may be vulnerable or exploited, especially on less secure or experimental networks). Additionally, transaction costs and staking commissions are not included in the analysis, but these fees will accumulate over time.
Conclusion
This analysis shows that staking rewards represent a unique and potentially profitable source of income for digital asset portfolio construction. Integrating them into a portfolio construction framework can enhance total return potential and provide income diversification benefits independent of traditional interest rate dynamics.
 Kikyo
Kikyo





