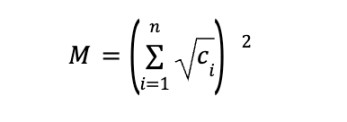Written by: Gate Research Institute
Foreword
On December 23, 2024, major exchanges announced their support for BIO Protocol and officially opened trading in January of the following year. This move officially brought DeSci (Decentralized Science) into the public eye. According to CoinGecko data, as of January 5, 2025, the market value of the DeSci track has reached US$2.37 billion, and 15 projects have increased by more than 30% in 7 days, such as PsyDAO, CRYORAT and GenomesDAO GENE, which have increased by more than 100% [1].
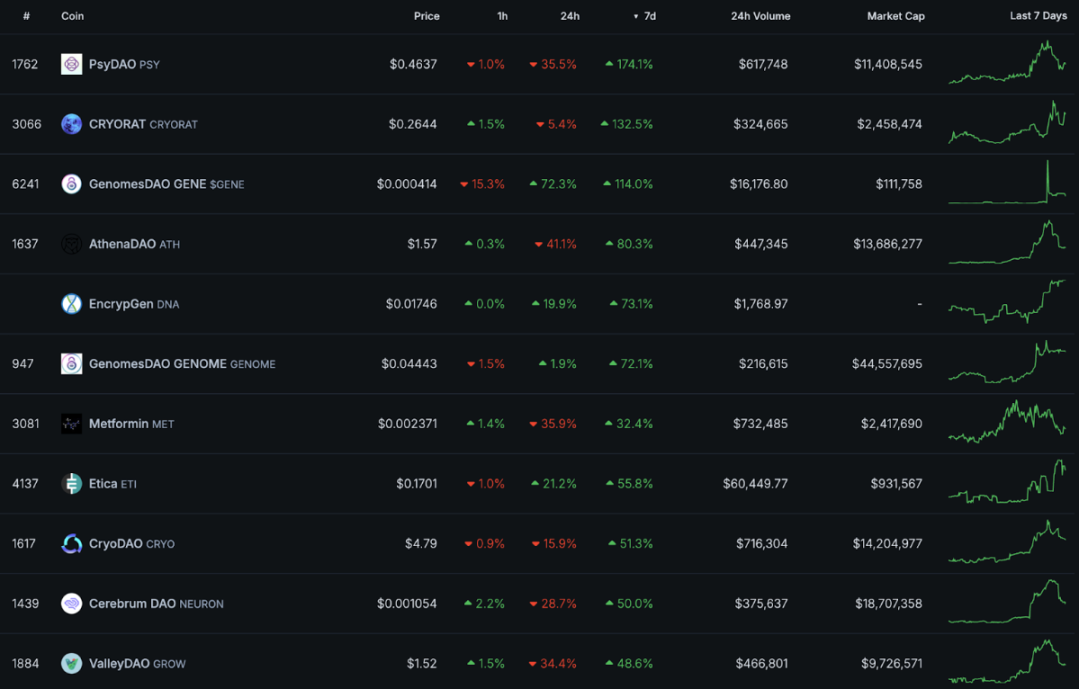
Figure 1: CoinGecko #DeSci classification data
On the other hand, the entire DeSci market value is only 2.37 billion US dollars (ranked 116 in CoinGecko Categories), and BIO Protocol has a market value of more than 1.12 billion US dollars, accounting for 47.25% of the total market value. Most of the others are small-cap projects with a market value of tens of millions or millions of US dollars. Therefore, it is not difficult to see that DeSci is still in its early stages of development, but has huge potential.
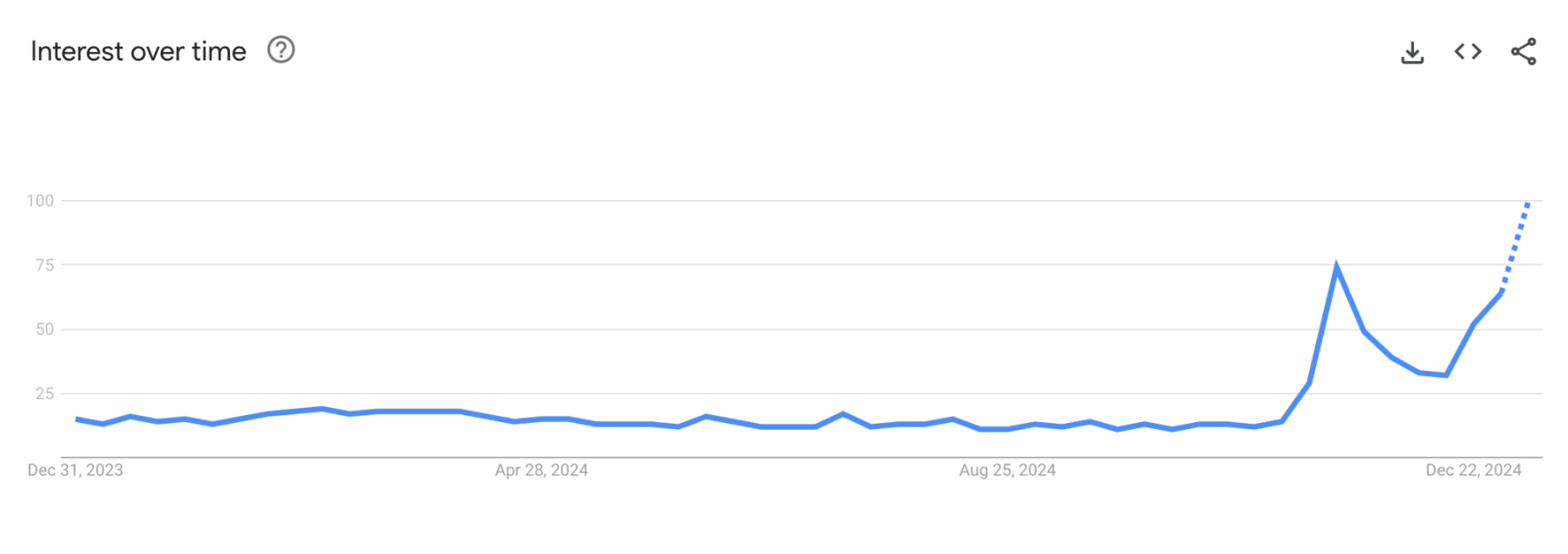
Figure 2: Search results for the popular search term DeSci on Google Trends
Origin: "Valley of Death" and "Elum's Law"
Before discussing DeSci, let's first understand two theories that shackle traditional medical science - "Valley of Death" and "Elum's Law".
The so-called "Valley of Death" refers to the huge gap between scientific discovery and the transformation of research results into innovations that can be used by patients [2]. The discovery process of a therapeutic drug needs to go through at least the following necessary and cumbersome processes: discovery phase, target validation, lead compound optimization, process chemistry, preclinical development, Phase I clinical trials, Phase II clinical trials, Phase III clinical trials, FDA application and approval. In order to cross this "valley of death", research projects must find suitable investors to provide financial support and overcome other operational challenges to eventually bring products to market.
However, even if products are successfully launched, they are usually sold to consumers at high prices. Therefore, the "valley of death" can be regarded as one of the important obstacles for traditional science to move towards a popular market.
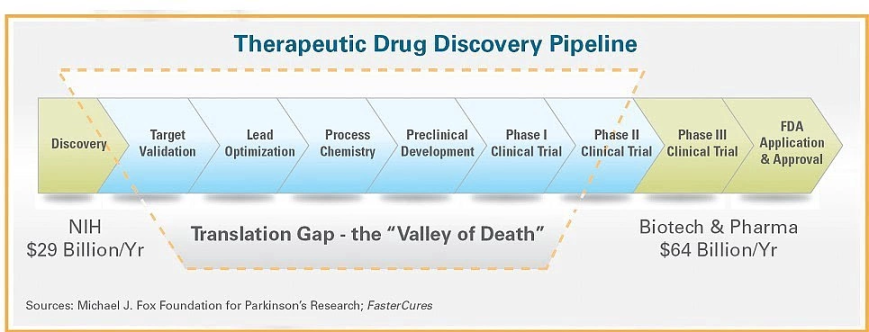
Figure 3: Valley of Death [3]: A therapeutic drug discovery process
Another manifestation of the shackles of traditional science is reflected in "Elum's Law" [4]. Many people are familiar with "Moore's Law", which states that the number of transistors in dense integrated circuits doubles approximately every two years, which roughly describes the exponential growth in computing power that people have seen over time.
Elum's Law is exactly the opposite. It suggests that powerful forces have overwhelmed advances in science, technology, and management over the past 60 years, or that some advances are not as "progressive" as people generally believe [5]. Over time, drug discovery has become slower and more expensive. While technologies such as high-throughput screening, combinatorial chemistry, and computational drug design should increase the rate of innovation, progress is bottlenecked by other systemic and institutional issues, such as increased regulatory burdens, a lack of open source shared technologies, and inappropriate capital allocation by existing companies, which hinder the entry of new drugs into the market and thus affect patients [6].
It is precisely because of the above theoretical problems in scientific and medical development that people urgently need to find ways to improve. Especially during the COVID period, the virus spread rapidly, and the continuation of human civilization is racing against the speed of virus mutation and transmission. Traditional medical discovery can no longer adapt to this challenge. Therefore, in times of crisis, Fast Grants (a rapid grant program launched in response to the COVID-19 epidemic) which is highly consistent with the core values of DeSci came into being [7]. The project was launched in April 2020 by Tyler Cowen, professor of economics at George Mason University, Patrick Collison, co-founder of the online payment processing platform Stripe, and Patrick Hsu, a bioengineer at the University of California. It has received donations from many entrepreneurs and organizations such as Arnold Ventures, The Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (an organization established by Zuckerberg and his wife), Patrick Collison (co-founder of Stripe), Jack Dorsey (founder and former CEO of Twitter), and Elon Musk. However, due to the lack of additional funding, new applications for Fast Grants have been suspended since January 2022. However, the practice of Fast Grants has had a profound impact on rapid scientific research. The founder of Arcadia Science directly pointed out that "the COVID pandemic has inspired a sense of urgency, collaboration, and enthusiasm for scientific progress beyond our conventional cognition. The resulting vaccine development proves how powerful cooperation between scientists is." It can be said that the misfortune of all mankind also directly promoted the birth and development of DeSci.
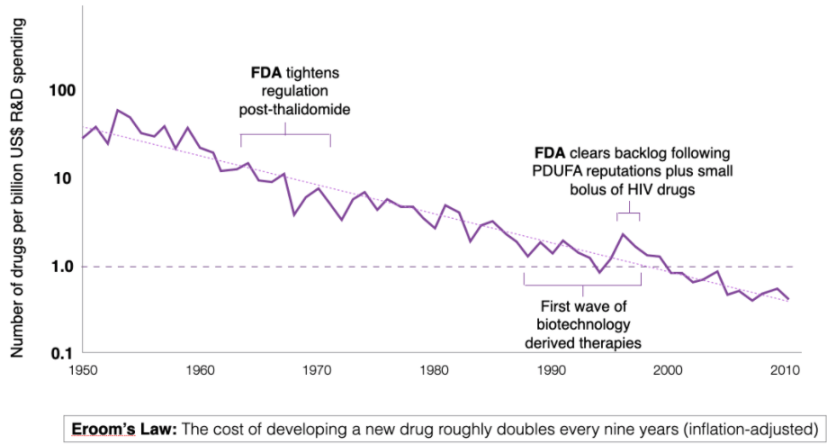
Figure 4: Elum’s Law【8】
DeSci Archaeology: A “Long-standing” Movement
According to Dr. David Koepsell, founder and CEO of EncrypGen【9】, the term DeSci was borrowed from “DeFi (decentralized finance)” and was first used publicly in a Youtube AMA on February 26, 2021【10】, and the DeSci tag was used in its company’s tweets in April. Although some project repositories containing DeSci began to appear on Github in March 2021 [11], the adoption of the term was still slow at the time.
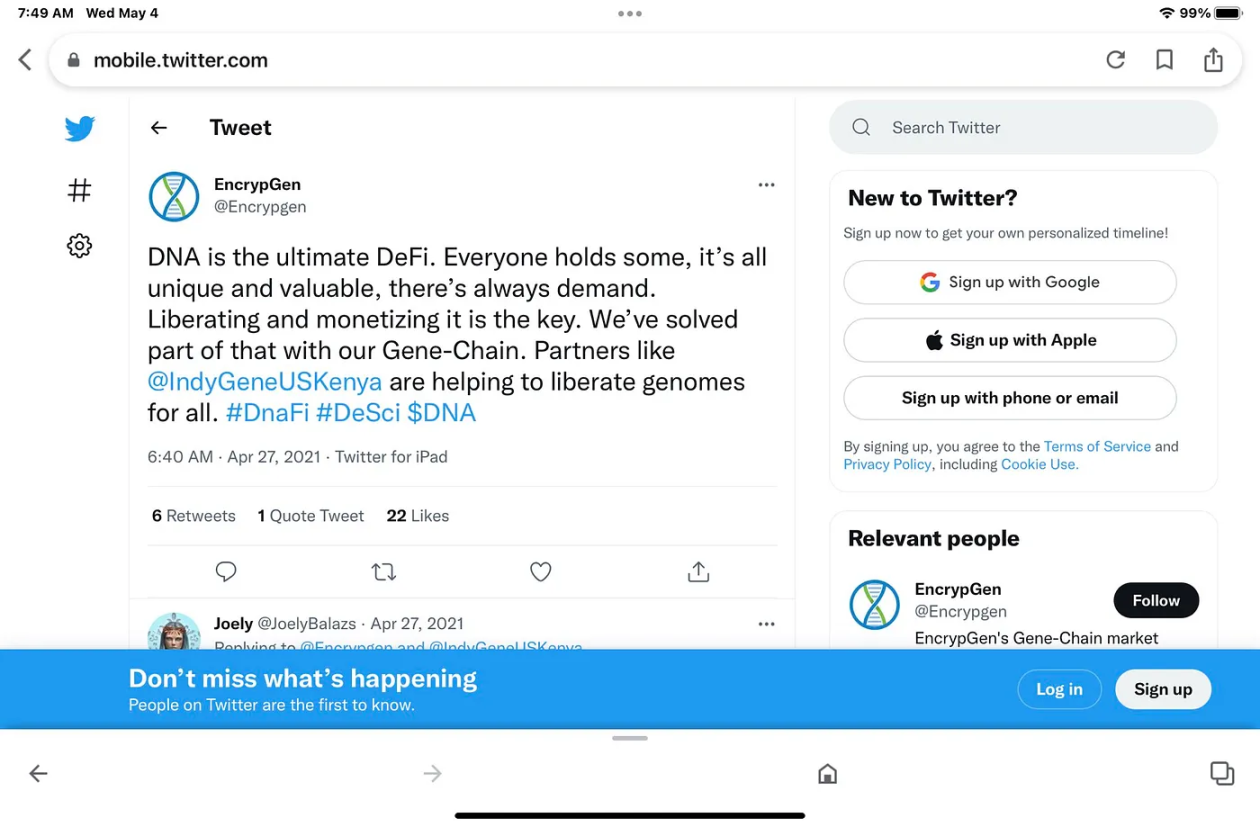
Figure 5: The DeSci tag that first appeared on Twitter [12]
The spirit of Desci is derived from "Science 3.0", which means "faster, more transparent, and more democratic". But the origin of this concept must be traced back to 20 years ago.
In 2004, Dr. Koepsell co-taught a course at the University of Buffalo called “Research Integrity: Why Good Scientists Do Bad Things” with Dr. David Triggle (and in 2008 became a tenured associate professor at Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands, dedicated to research and writing on research integrity). The course focused on the scientific spirit proposed by Robert Merton. Merton studied the workings, institutions and processes of science and argued that in order to be successful, science must follow four main principles: organized skepticism, universalism, community attention and selflessness. He called these the “spirit” of science [13].

Figure 6: On SOCIAL STRUCTURE AND SCIENCE【14】
In 2010, Dr. Koepsell published Back to Basics: How Technology and the Open Source Movement Can Save Science【15】in Social Epistemology, Vol. 24, No. 3. In this article, Dr. Koepsell proposed that the Internet, especially Wiki technology, can help solve problems related to the scientific spirit and better embrace the scientific spirit through the concept of "Science 3.0".
Kopespell's speech at his alma mater in 2016 led to the creation of EncrypGen (the company was acquired by IndyGeneUS.ai in December 2022). Because of the emergence of Ethereum in 2016, the idea of applying blockchain to the 2010 paper became a reality. EncrypGen allows users to purchase DNA data using Tokens, making the use of DNA data in science "faster, more transparent, and more democratic."
Tracing back to its roots, this should be one of the earliest experimental projects in the DeSci track: a market for de-identified genomic data that eliminates large data brokers and allows peer-to-peer sales and settlement of DNA data searches and transactions anywhere in the world using the native cryptocurrency $DNA.
The establishment of Molecule in 2018 has enabled DeSci to achieve real development. It can be said that almost all of DeSci's current projects are inextricably linked to Molecule and its team. Its founder and CEO Paul Kohlhaas is also the founder of BIO Protocol and a core contributor to VitaDAO. Of course, he has also worked at ConsenSys, and the company is no stranger to Web3 users. Its incubated Metamask is the most user-friendly crypto wallet application. Tyler Golato, another founder of Molecule, is a true scientist with unique attainments in the research of biochemistry, molecular biology and biological geriatric diseases. He is also a partner of Triplicate and a co-founder of VitaDAO and BIO Protocol. Molecule's earliest exploration was during the NFT bull market cycle. They hope to solve problems such as the opacity of intellectual property rights in traditional medicine through NFT solutions (which will be discussed later). According to Molecule’s official website, more than a dozen projects have received funding through the sale of IPT [16].
Three years later, in 2021, VitaDAO was established. If Molecule has greatly promoted the development of DeSci, then VitaDAO is a landmark project that truly integrates "De" (decentralization) and "Sci" (science), as can be seen from its financing background.
The Fast Grants project mentioned above has received support from many entrepreneurs and organizations, among which Vitalik Buterin (founder of Ethereum) has also actively participated in related discussions. As a technology pioneer who has long been concerned about the field of longevity, Vitalik has great enthusiasm for promoting related research. The dream of Balaji Srinivasan, former CTO of Coinbase, is to build a brand new country [17], a vision that is also inseparable from the innovation of science and technology. In addition, the destructiveness of the new crown epidemic has prompted people to be more eager to pursue a healthy and long-lived lifestyle.
Against this backdrop, VitaDAO has become a project that combines these concepts and goals. It has not only attracted investments from Vitalik and Balaji, but has also received support from Pfizer Ventures, fully demonstrating the cross-field integration from blockchain technology, capital power to life sciences. The birth of this project marks an important breakthrough for DeSci in terms of concepts and practices, and also establishes its core position in promoting longevity research and technology development.
Pfizer Ventures (PVI) is the venture capital arm of Pfizer, focusing on investing in emerging companies that are developing transformative drugs and technologies. Some Web3 users may be unfamiliar with Pfizer. As a giant in traditional biomedical companies, Pfizer was founded in 1984, with a history of more than 100 years and is headquartered in New York. In 2022, Pfizer ranked fourth on Fortune's annual list of "World's Most Admired Companies"; in PatientView's global survey, Pfizer ranked second among large biopharmaceutical companies; and ranked fourth in the 2021 Access to Medicines Index pharmaceutical company list (data as of February 2022) [18]. At the same time, it is also the largest R&D-based multinational biopharmaceutical company in China, having introduced more than 50 innovative drugs to China, with operations in more than 300 cities, and its anti-infective and cardiovascular drugs ranked first in the Chinese market [19]. Therefore, VitaDAO is the product of the cooperation between Web3 "giants" and traditional medical "giants".

Figure 7: Pfizer
It is not difficult to see from the development history of DeSci that its development is not achieved overnight. From the initial modern scientific spirit concept, to the development of blockchain technology that allows traditional science and traditional medical practitioners to see opportunities for change, and then to the final integration, it has been 20 years. Although the previous road was very slow, with the birth of VitaDAO and BIO Protocol, DeSci ushered in its first acceleration moment.
DeSci Big Bang: Towards a Hundred Schools of Thought
The previous article talked about the "Valley of Death" and "Elum's Law". There is a huge gap between traditional scientific research and the market. The fundamental reason is that researchers find it difficult to obtain financial support in the traditional capital field. Investment institutions may be more willing to support research on diseases that are difficult to cure in order to obtain rich returns. In 2018, Goldman Sachs released a report titled "Genome Revolution", questioning whether curing patients is a sustainable business model. Goldman Sachs took Gilead Sciences as an example. The company generated $12.5 billion in revenue in 2015 for developing an effective hepatitis C treatment drug, but as more and more patients were cured, sales fell sharply to $4 billion in the following years [20]. This situation has hindered the development of many scientific projects and prevented them from obtaining financial support.
However, after VitaDAO gained the attention of Web3 "giants" and traditional medical "giants", BIO Protocol was established in 2022 and attempted to fundamentally alleviate this problem.
BIO is the management and liquidity protocol of DeSci. Its mission is to accelerate the development of biotechnology by enabling a global community of patients, scientists, and biotechnology professionals to jointly fund, build, and own tokenized biotechnology projects and intellectual property (IP). BIO aims to catalyze the on-chain scientific economy through decentralized funding, incentives, and liquidity. BIO tokens enable holders to access BIO's scientific community and IP network, thereby gaining broad exposure to the DeSci economy [21].
As of January 7, 2025, BIO Protocol has helped 8 projects raise more than US$30 million, of which more than US$7.2 million was directly deployed in research fields [22]. Below you can take a quick look at which projects BIO Protocol has supported and what substantial progress these projects have made after receiving funding, so as to understand the important role BIO plays in DeSci.

Figure 8: Projects incubated by BIO Protocol
PsyDAO
PsyDAO has built a community dedicated to the evolution of consciousness through safe and accessible psychedelic experiences, and provides funding for early research and intellectual property in the field of psychedelic drugs to promote its democratization.
Many readers may have an instinctive resistance to the term "psychedelic drugs", mistakenly confusing it with psychoactive substances such as drugs. However, according to Joseph La Torre, a psychology doctor from the University of Ottawa, at a conference at Harvard Medical School, "psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy has potential benefits and risks for people with mental illness" [23]. Although it is generally believed that psychedelic drugs can cause psychosis and catalyze the onset of psychotic symptoms in people. However, this has been shown to occur only in cases of natural use and general abuse, and there is a lack of evidence of these effects in controlled and clinical environments.
According to PsyDAO's financing BP in BIO Protocol [24], currently 20% of the world's population suffers from varying degrees of mental illness. In 2024, global investment in psychedelic drug companies will exceed US$200 million, and it is expected that in 2031, the total market value of psychedelic drugs will reach US$7 billion.
In order to promote psychedelic drug research, in May 2023, PsyDAO announced that it hoped to raise US$300,000 to US$1 million. However, with the help of BIO (which is why Binance invested in BIO [25]), PsyDAO raised 661 ETH (more than US$2 million) by selling 20% of PSY tokens in November 2024. This also confirms that BIO Protocol helped the DeSci project it incubated solve the funding problem.
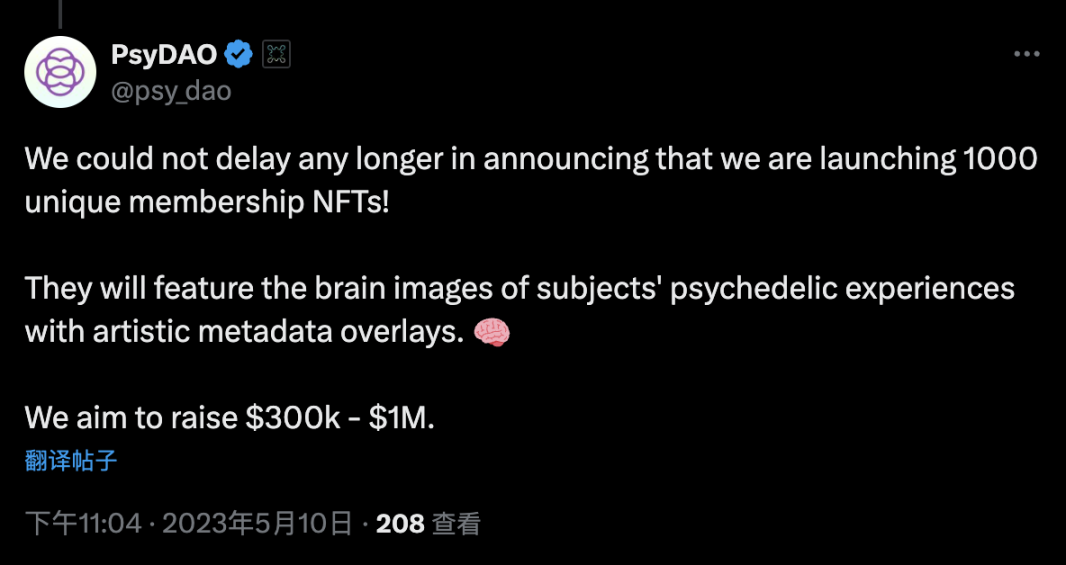
Figure 9: PsyDAO’s financing target in 2023 [26]
It is not difficult to see from PsyDAO’s Roadmap that after being incubated by BIO Protocol, its project has achieved one milestone after another. In the fourth quarter of 2024, it completed financing and launched its first IP token - BeeARD, funded OPSY (an open data collection platform for survey-based psychedelic research), and decided to fund the research of the next generation of psychedelic drugs in the first quarter of 2025, and planned to open a cultural portal in the Amazon region of Pucallpa, Peru. This also shows how much the rapid financing model provided by BIO Protocol has helped the DeSci project.
Finally, there is an interesting thing about PsyDAO, that is, the supply of its token $PSY is 102,334,155. 10,233,415 is the 40th ring of the Fibonacci sequence. 40 is a sacred number in many religions [27], representing the journey of transcendence and integration of individuals (40 days and nights) and the collective (40 years of desert life) [28]. This interpretation also gives the PSY token a bit of meme color.
CryoDAO
Perhaps influenced by many science fiction movies such as "Interstellar", the author has always had a longing for human hibernation. CryoDAO is related to this. It focuses on funding and incubating technical projects related to human cryonics.
The concept of cryonics has a long history. In 1962, physics professor Ettinger expounded this concept in his book "The Prospect of Immortality". The first person to try cryonics was psychology professor James Bedford, who died of cancer in 1967 at the age of 73. But when you read this, "he" is in a barrel of liquid nitrogen in Arizona, continuing to "exist in the world" in another way.
Here may be a brief explanation of what cryonics is. Cryonics is low temperature. Some people who cannot accept complete death can freeze their bodies, let their body metabolism stagnate, and hope that people from the future can bring them back to life through future technology.
But cryonics is a "rich man" game. There are currently about 8 legal cryonics organizations in the world, and most of them are expensive. For example, Alcor's freezing fee is about 200,000 US dollars, while CI's fee is nearly 100,000 US dollars. Non-profit organizations need to conduct research and screening, and only those who meet the target group can conduct human cryonics experiments. It can be seen that human cryonics is still a long way from being popularized.
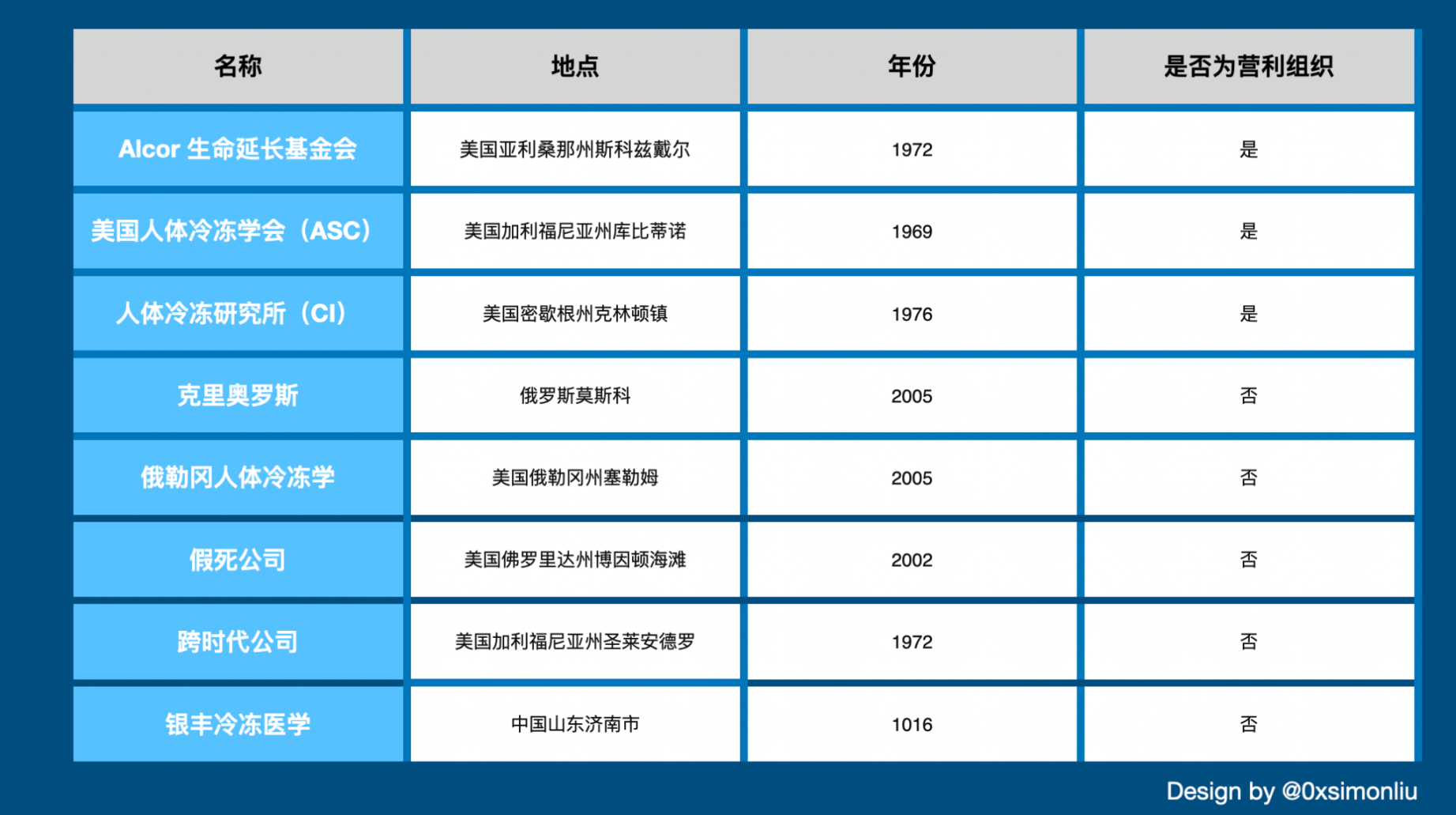
Figure 10: Global cryonics-related companies
Despite this, people still have great enthusiasm for cryonics. On January 16, 2024, with the help of BIO Protocol, CryoDAO raised a total of 1,108 ETH.
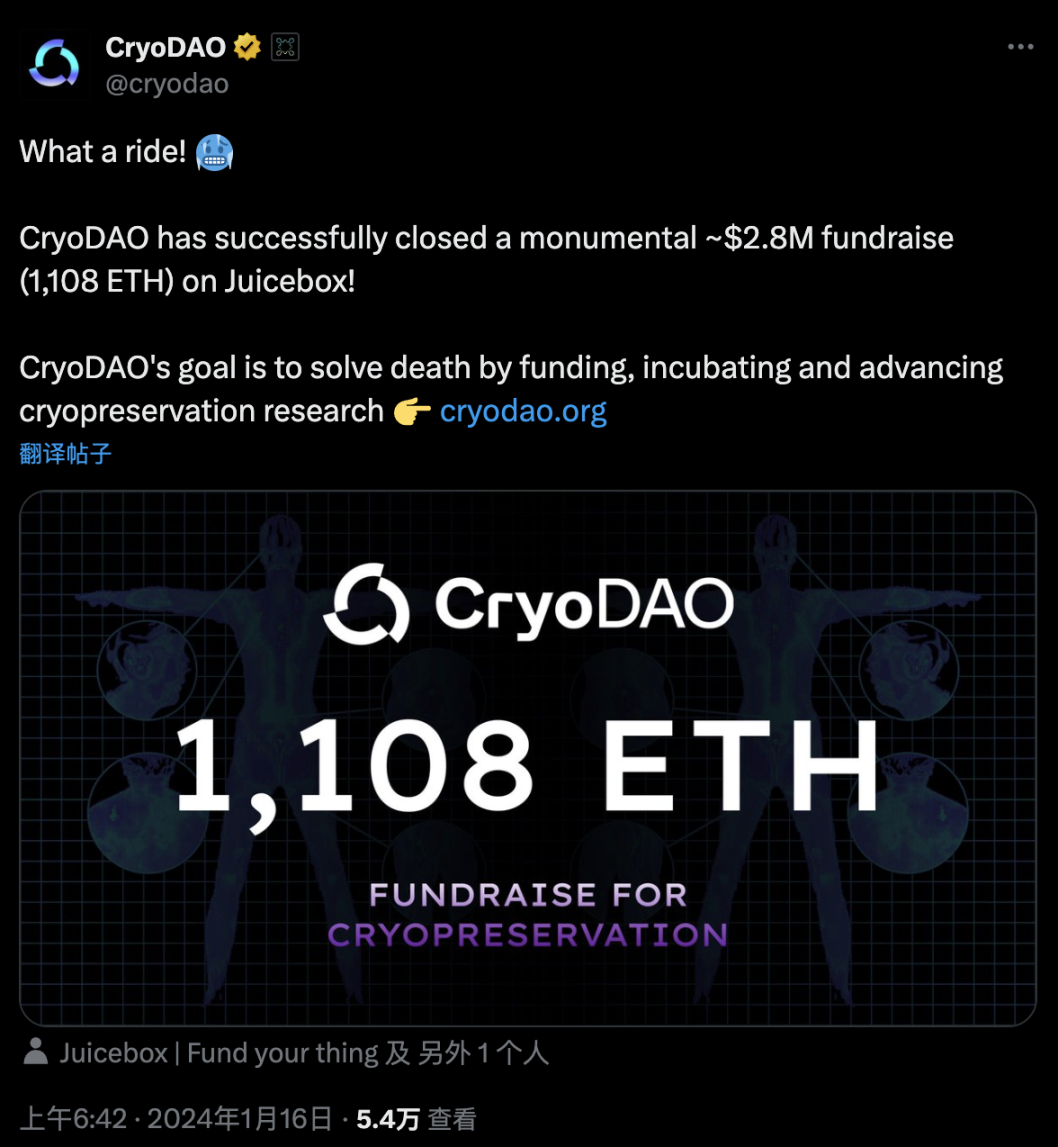
Figure 11: CryoDAO received 1108 ETH financing [29]
After obtaining considerable financing, CryoDAO also expects to launch a series of actions in 2025, including launching the IceBreaker podcast, popularizing knowledge about cryonics, achieving live births in large mammals through vitrification and ovarian transplantation, launching the second IPT, launching a CPA database for researchers and medical professionals, launching a first-level space cryogenic sleep conference, etc.
In addition, CryoDAO's token CRYO also has a good market performance. According to CoinGecko data, as of January 7, 2025, the market value has reached 16.52 million US dollars, an increase of 108.8% in 30 days.
AthenaDAO
Women's health has always been an important social and political topic, but it is often overlooked in real social life [30]. In the 2020 budget of NIH, the percentage of funds allocated to women's health research accounted for only 10.8% [31]. On the other hand, women have strong medical purchasing power. According to statistics from the US Department of Labor in 2018 [32], in 2015, the medical expenses of women aged 19-44 were more than 80% higher than those of men of the same age (this may be more related to female reproduction, but it also brings related health problems). In addition, according to IBISWorld statistics in 2023, women's purchases have driven the development of the second largest revenue industry in the United States, including the wholesale industry of pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and toiletries (about US$500 billion [33]). These data are enough to show the amazing potential and explosive power of women's health care in the commercial road.
In addition, in the current existing women's health market, there is also the problem of uneven resource allocation. For example, although the patients affected by menopause are the most, the investment in its research is far less than that in ovarian cancer research (possibly more than 375 times [34]). Although cancer is indeed a terrifying disease, considering the huge amount of research and development funds invested in this field, but the progress made is relatively limited, it is still worth pondering whether this resource allocation is reasonable.
AthenaDAO is committed to solving the above problems and raised $100,000 on BIO Protocol in 2023 and another $250,000 from early supporters to invest in three different IP NFTs [35]. Despite the small scale of financing, $ATH’s market performance cannot be ignored. According to CoinGecko data, as of January 7, 2025, $ATH has achieved an increase of more than 192% in the past year. Currently, although the market has certain potential, its market value is still only $14.86 million.
HairDAO
Among many DeSci projects, HairDAO’s research field is perhaps the most popular and influential. It was founded in November 2021 and is also one of the pioneers of DeSci. As its name suggests, HairDAO is focused on addressing the global problem of hair loss. Although hair loss is not a major focus of traditional scientific research, it affects nearly 60% of the world’s population. According to HairDAO, 66% of men will experience noticeable hair loss before the age of 35, while 50% of women may also face hair loss in their lifetime [36]. Despite the extremely common problem of hair loss, research in this area has long been underfunded, and there has been almost no new drug development progress in the field of hair loss treatment since the introduction of finasteride in 1997. Surprisingly, only 0.03% of all early R&D funds were used for hair loss research, which is only about US$5.4 million per year. Because hair loss is often classified as a "cosmetic disease" rather than a medical disease, this research area has long been neglected. However, hair loss is not just a cosmetic problem. Its profound impact on mental health has been widely confirmed - there is a high correlation between mental health problems and hair loss, reflecting its indirect impact on overall human health.
The prevalence of the problem contrasts sharply with the lack of resources invested, and also exposes a huge market gap in this field. HairDAO aims to bridge this gap by establishing an open source R&D network. This network brings together patients and researchers, combining the power of the community to jointly develop innovative hair loss treatments. Through a decentralized collaboration model, HairDAO not only accelerates the development of hair loss treatments, but also drives more funds and resources to this neglected field, bringing new hope to hair loss patients around the world.
In addition to issuing tokens and building DAO organizations. HairDAO has also explored IP-NFT. As one of the early projects supported and incubated by BIO, it conducted its first IP-NFT transaction in February 2023. This makes HairDAO the second BIO DAO project to conduct IP-NFT transactions after VitaDAO [37].
In addition, $HAIR has also shown significant performance in the development of DeSci. According to Geckoterminal data, $HAIR has risen from a low of about $2 to a high of nearly $149 ($89 as of January 10, 2025), an increase of more than 7,000%.
BIO has also incubated many excellent DeSci projects such as ValleyDAO, Quantum Biology DAO, Long Covid Labs, etc. Due to the ability to quickly obtain open funding assistance, more and more DeSci projects have emerged. According to the ecological map in Wiki 101 compiled by Jocelynn Pearl, there are currently 132 DeSci projects, showing a situation of a hundred schools of thought.
Figure 12: DeSci Ecosystem Map [38]

In November 2024, Zhao Changpeng and Vitalik attended a cooperation meeting between Binance Labs and BIO Protocol in Bangkok. After the meeting, Zhao Changpeng expressed his hope to see 1,000 DeSci projects next year [39]. It can be foreseen that, driven by strong capital, DeSci is expected to achieve further development in 2025. However, there is still uncertainty as to how long this development can last. Whether DeSci is just a short-term trend, or can it become a breakthrough for Web3 to innovate traditional industries like DeFi, is worth further discussion.
De + Sci: How to "decentralize" science?
Although the previous article talked about the "Valley of Death" and "Elum's Law", it has not fully sorted out the substantive problems in traditional science or traditional medicine, and thus cannot fully view the necessity of combining Web3 with science. Therefore, to prove that DeSci will become an important narrative in the future development of Web3, it is necessary to prove that Web3 is one of the best solutions to solve traditional scientific problems. Let's take a look at the problems that exist in the complete life cycle of traditional science and how Web3 solves them.
Problems in the development of traditional science
Scientific dilemma caused by capital
Uneven distribution of scientific research funds
According to Bloch and Sorensen’s 2015 academic research report The size of research funding: Trends and implications [40], the trend of funding concentration at the individual and group levels is prevalent in a wide range of countries [41]. Katz and Matter further demonstrated this in their 2017 academic study On the Biomedical Elite: Inequality and Stasis in Scientific Knowledge Production [42]. They believed that the funding inequality of the National Institutes of Health in the United States increased significantly from 1985 to 2015, and a small number of researchers and institutes accumulated more and more funds. Uneven distribution of funds will inevitably limit scientific diversity and innovation. At the same time, overly concentrated allocation of scientific research funds will also form a Matthew effect, that is, well-known research institutions and researchers are more likely to obtain financial support, which will further aggravate the concentration of resources [43]. Table 1 shows the support arguments of various researchers for "scientific funds should be dispersed rather than overly concentrated" from multiple angles.
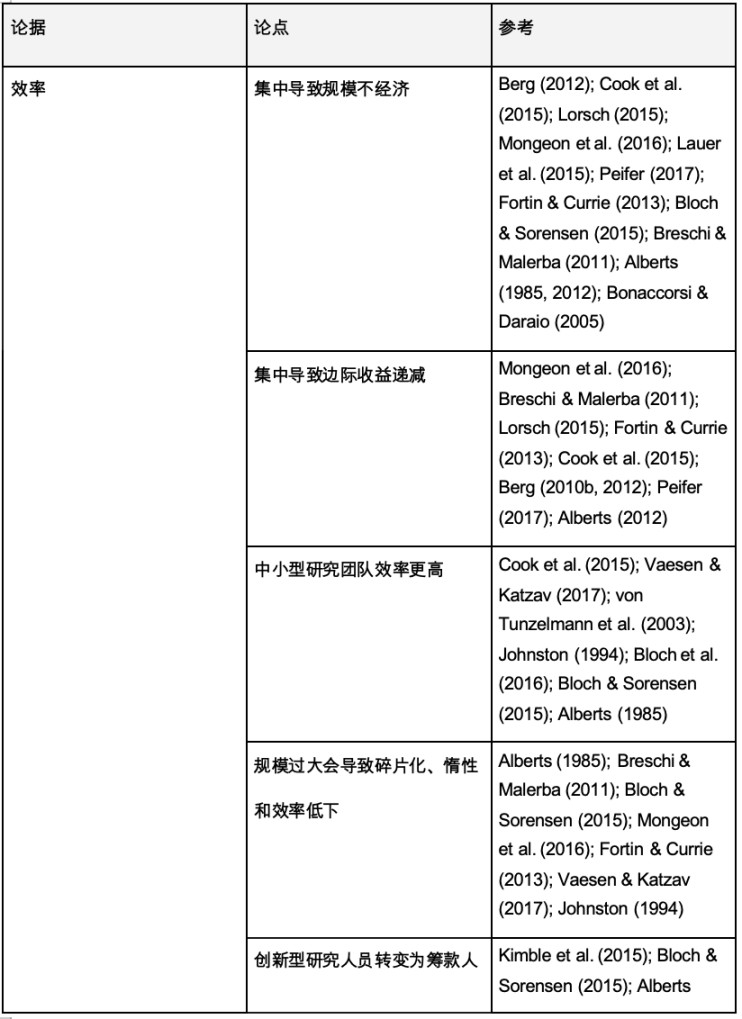
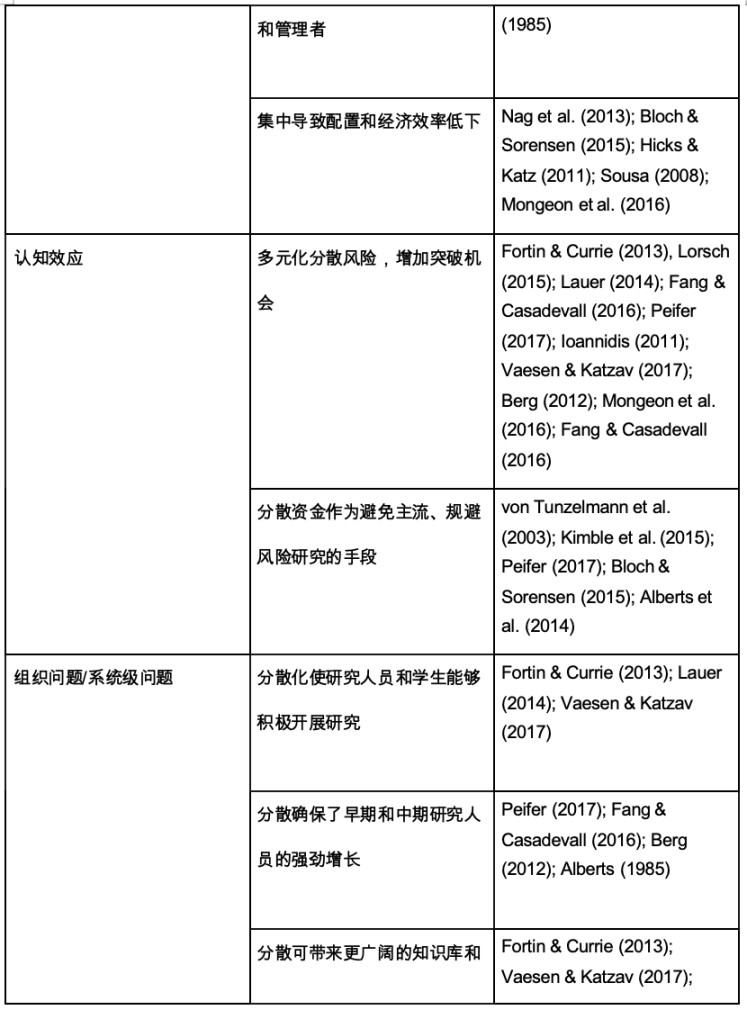
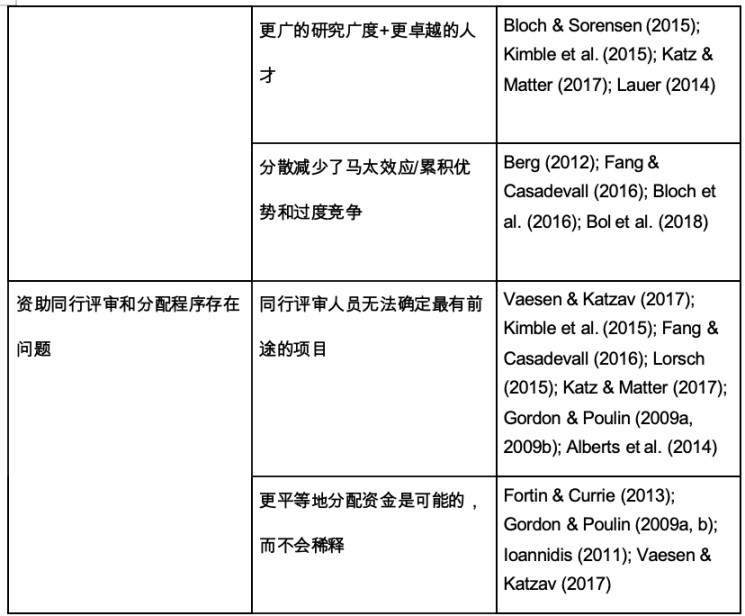
Table 1: Support for the view of decentralized scientific research funding [44]
Capital restricts cooperation
Funding agencies are often profit-oriented and restrict cross-institutional cooperation, which fragments scientific research and hinders knowledge exchange and sharing. Because when funders prioritize their own interests, they may tend to support research projects that are directly related to them and ignore cross-disciplinary or cross-institutional cooperation. This practice may cause researchers to work in isolation in their respective fields, lack interaction with other disciplines or institutions, and form so-called "research islands". At the same time, this may cause different research teams to repeat "reinventing the wheel" on similar topics, wasting resources and time. On the other hand, cross-disciplinary and cross-institutional cooperation is often a source of innovation. When funders restrict such cooperation, it may hinder the generation of new ideas and technological breakthroughs. Funding strategies that restrict cooperation may lead to the dissemination of research results in a small range, hindering the widespread sharing and application of knowledge.
For example, one study pointed out [45] that organizational factors play a key role in the research cooperation network of higher education institutions. When the funding strategy does not encourage cross-institutional collaboration, it may lead to research fragmentation and hinder the creation and dissemination of knowledge.
Inefficient funding, limited transparency, and few funding mechanisms
The approval process for scientific research projects is cumbersome, causing researchers to spend a lot of time and energy on applying for funding, affecting scientific research efficiency. Scientific research funding usually involves multiple levels of review, including preliminary review, expert review, interview and defense, etc. Each stage takes time, which prolongs the overall approval cycle. In addition, applicants need to prepare a large amount of written materials, such as research plans, budget reports, and ethical reviews, which increases the time cost. Due to the large number of applicants, the review committee needs more time to screen and evaluate, further prolonging the decision-making time.
In addition, the lack of transparency in the allocation process of scientific research funds leads to irrational resource allocation and even corruption. Including opaque review criteria, lack of feedback mechanism, and internal personnel preferences. These problems limit the enthusiasm and innovation ability of researchers and hinder the progress of scientific research.
Peer review is unpaid, for-profit publishers profit
Peer review relies on researchers to voluntarily provide their time and expertise, usually without any compensation. Due to the lack of financial incentives, reviewers may not devote enough time and energy, resulting in delays in the review process and even affecting the quality of the review [46]. In addition, studies have shown that scholars from developed countries are more likely to participate in reviews, while scholars from developing countries are unable to undertake unpaid review work due to economic pressure [47].
However, many commercial publishers make huge profits by charging high subscription fees and open access fees (APCs). For example, the high subscription fees of some well-known journals make it difficult for academic institutions and individuals to afford them, limiting the dissemination of knowledge [48]. In order to make articles open access, authors or their institutions need to pay high APCs, ranging from hundreds to thousands of dollars, which increases the financial burden on researchers [49]. Moreover, the profit margins of major academic publishers often exceed 30%, which is much higher than many other industries, indicating the high profitability of academic publishing [50].
Scientific opacity
Transparency in scientific research is a key factor in ensuring research quality, promoting knowledge sharing and advancing scientific progress. However, the following problems still exist in current scientific research practices.
Sharing of laboratory resources is slow and opaque
Sharing of laboratory resources is crucial to improving scientific research efficiency and promoting cooperation. However, the resource sharing process is often slow and lacks transparency. For example, many research data are not made public, which limits the verification and further research of other researchers. In addition, the data formats and management methods of different laboratories are different, which increases the difficulty of resource sharing. In addition, the lack or imperfection of sharing platforms and tools hinders the effective sharing of laboratory resources. Open science advocates data sharing to improve the transparency and reproducibility of scientific research results.
Inefficiency and bias in academic publishing
Inefficiency, bias and exploitation in the academic publishing process have seriously affected the dissemination of scientific research results and the healthy development of the academic ecosystem. For example, studies have shown that positive results are more likely to be published than negative results, leading to systematic bias in scientific research literature [51]. This leads researchers to tend to report meaningful results while ignoring findings that do not support the hypothesis, further exacerbating the incompleteness of the literature.
Opaque intellectual property
The opacity of the ownership and use rights of intellectual property (IP) of scientific research results stems from a variety of factors, such as the complexity of multi-party cooperation. Modern scientific research projects usually involve multiple research institutions, sponsors and individuals. In the absence of clear agreements, determining the ownership of intellectual property rights of each party becomes complicated and prone to disputes. In addition, there are differences in intellectual property laws in different countries and regions. In international cooperation projects, participants may have different understandings of the ownership and use of intellectual property rights, which increases opacity. Most importantly, research institutions and companies may choose not to disclose information related to intellectual property for competitive reasons, making it difficult for the outside world to understand its ownership and use.
The scientific process is opaque, and people can only see successful experiments
The process of scientific research often lacks transparency, resulting in failed experiments and negative results not being fully recorded and disseminated. The academic community tends to publish positive results and ignore negative or non-significant research findings. This phenomenon is called "publication bias" or "drawer effect". This will lead to other researchers repeating the same experiments due to the lack of disclosure of negative results, wasting resources and delaying scientific progress, and it also fails to fully reflect the actual situation in the research field.
Failed experiments also provide important scientific information and help improve theories and methods. For example, in an electrochemical system, researchers found that the failure results under certain experimental conditions revealed problems with oxygen mass transfer, which led to improved experimental design and success [52].
The above mentioned many problems in traditional science, which have hindered the development of science and human progress to varying degrees. So how does Web3 solve these problems?
How does Web3 solve traditional scientific problems?
Quadratic donations and crowdfunding to solve the problem of uneven capital distribution
Quadratic Funding (QF) is a public goods funding mechanism widely used in the Web3 ecosystem, proposed by Glen Weyl and others. Its core idea is to reduce capital monopoly and optimize the efficiency of capital allocation through the weighted allocation of small donations from the community and matching funds. The following is the QF formula, where M is the funds allocated to a project in the matching pool, and ci represents the amount of donation made by each donor i to the project:
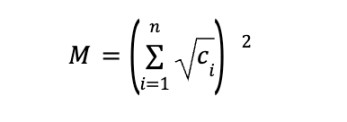
As mentioned above, under the traditional funding model, large institutions usually dominate scientific research projects with a single huge donation, forming a Matthew effect (the rich get richer). QF emphasizes the collective role of small donors. Even if the individual donation amount is small, as long as the number of donors increases, the matching funds will increase significantly. This model encourages communities and individuals to actively participate in scientific research funding and weakens the funding monopoly of a single institution or individual.
Gitcoin is a successful example of the quadratic donation mechanism. As of January 8, 2025, Gitcoin has raised a total of $60 million for more than 5,200 projects [53], of which more than 70% came from small donors of less than $10. Gitcoin also has a special DeSci round to raise funds for scientific research. Interestingly, the DeSci round in Gitcoin originated from the longevity round (GR12-GR14) [54]. In order to shift the focus to the broader DeSci system, GR15 began to have a dedicated DeSci round [55].
In addition to quadratic donations, BIO Protocol provides a Launchpad crowdfunding platform, which enables more scientific research projects, especially innovative and diverse projects, to obtain the necessary financial support. BIO Launchpad uses a batch auction mechanism [56]. Unlike traditional time-limited auctions (such as Dutch auctions), the price of a batch auction is determined by the demand of participants, and the final price is determined based on the bidding situation at different price levels. BIO Launchpad's auctions first set the total amount of tokens to be auctioned, which are usually used to help raise funds and implement the governance allocation of the DAO. Participants can choose the bid amount and price according to their wishes during the auction. After the auction ends, all bids are sorted in the following way: First, sort by bid price from high to low; If there are multiple bids with the same price, they are further sorted by bid amount from small to large. The final clearing price is the price at which the demand for all auctioned tokens is fully satisfied. The price is determined by simulating token allocations at different prices, as follows:
In the first iteration, tokens are allocated only to the highest bidder, and tokens are allocated according to their bids;
In the second iteration, tokens are allocated to the top two bidders according to the second highest price;
Each iteration will include all bidders at that price and above, and tokens are allocated according to the prices of this group of bidders. This process continues until all tokens are allocated, and the final clearing price is the price at which all tokens are fully allocated for the first time.
At the final clearing price, tokens are allocated in order starting with the bidder with the highest bid. Once all tokens have been allocated, the allocation process stops, although some bidders may bid higher than the final clearing price.
Through batch auctions, BIO Protocol allows individual investors around the world to participate in the funding of scientific research projects, which breaks the traditional funding allocation model dominated by a few large institutions. Through this market-based bidding process, the true value of the project is discovered, ensuring that funds are allocated to the most promising and supported projects. This improves the efficiency of fund use and avoids waste of resources. Recently, Quantum Biology DAO conducted a token auction through the Launchpad mechanism of the BIO platform. The auction ended on December 17. During the period, the bidding was very hot, and the starting price once exceeded the original bid by more than 10 times. This case demonstrates the effectiveness of the batch auction mechanism in attracting diversified funds and promoting fair competition [57].

Figure 13: BIO Protocol has helped 8 projects raise more than 30 million US dollars [58]
The quadratic donation and crowdfunding model solves problems such as excessive capital concentration, uneven distribution, low financing efficiency, and lack of transparency. The general public can participate in scientific development and supervise and promote scientific progress in the form of a community. This is a fundamental reform of "Sci".
Flexible smart contracts make peer review profitable
Peer review is an important guarantee mechanism for scientific progress, ensuring the rigor and credibility of scientific research. As mentioned above, in traditional science, since most peer reviews have no economic incentives, it has seriously hindered the development of science. Web3 technology brings a new decentralized solution to scientific publishing and peer review. Through smart contracts, token incentives and on-chain records, Web3 can significantly improve the transparency, fairness and efficiency of reviews.
Ants-Review is a privacy-oriented protocol based on the Ethereum blockchain that aims to promote an open, anonymous and decentralized peer review process. Authors can set rewards to attract reviewers to review their papers. After completing the task, reviewers will receive token rewards based on the quality of the review. The quality of the review is determined by voting by community members, and high-quality reviews will receive higher rewards, thereby encouraging reviewers to conduct serious and fair reviews. The review process is completely anonymous, which reduces the bias or conflict of interest caused by the identity exposure of the reviewer. Research shows that Ants-Review is superior to traditional review systems in terms of transparency and incentive mechanisms, and can effectively reduce review bias caused by human intervention [59].
In addition to Ants-Review, other decentralized peer review projects have emerged in the Web3 field. For example, Nature, one of the most influential journals in the world, highlighted the ResearchHub platform in its article on December 11, 2024, which provides peer reviewers with $150 worth of cryptocurrency for independent review of new research papers. This model has achieved positive results in practice. The article specifically mentions the case of Pedro Paulo Gattai Gomes, a molecular biology consultant in São Paulo. He said that the income from reviewing on ResearchHub has exceeded his income as a professor in an academic institution [60].
In addition, scholars Andreas Finke and Thomas Hensel proposed a community-owned peer review system [61], which improves the transparency and efficiency of reviews in the following ways:
Payment incentive mechanism to ensure that reviewers are paid;
Anonymous publication of review reports for community review and supervision;
Using blockchain to record reviewer contributions and establish a reputation system;
After completing the review, reviewers receive a digital certificate to enhance their academic reputation.
The system relies on the immutability of blockchain and flexible smart contracts to reduce human operational errors and biases and ensure that the review process is open and transparent.
IP-Token makes scientific intellectual property transparent
The management and distribution of intellectual property (IP) is one of the key challenges of traditional science. Molecule uses blockchain technology to achieve transparent and decentralized management of intellectual property rights of scientific research results by introducing intellectual property non-fungible tokens (IP-NFTs) and intellectual property tokens (IPTs), solving the problem of opaque ownership and use rights of intellectual property in traditional scientific research.
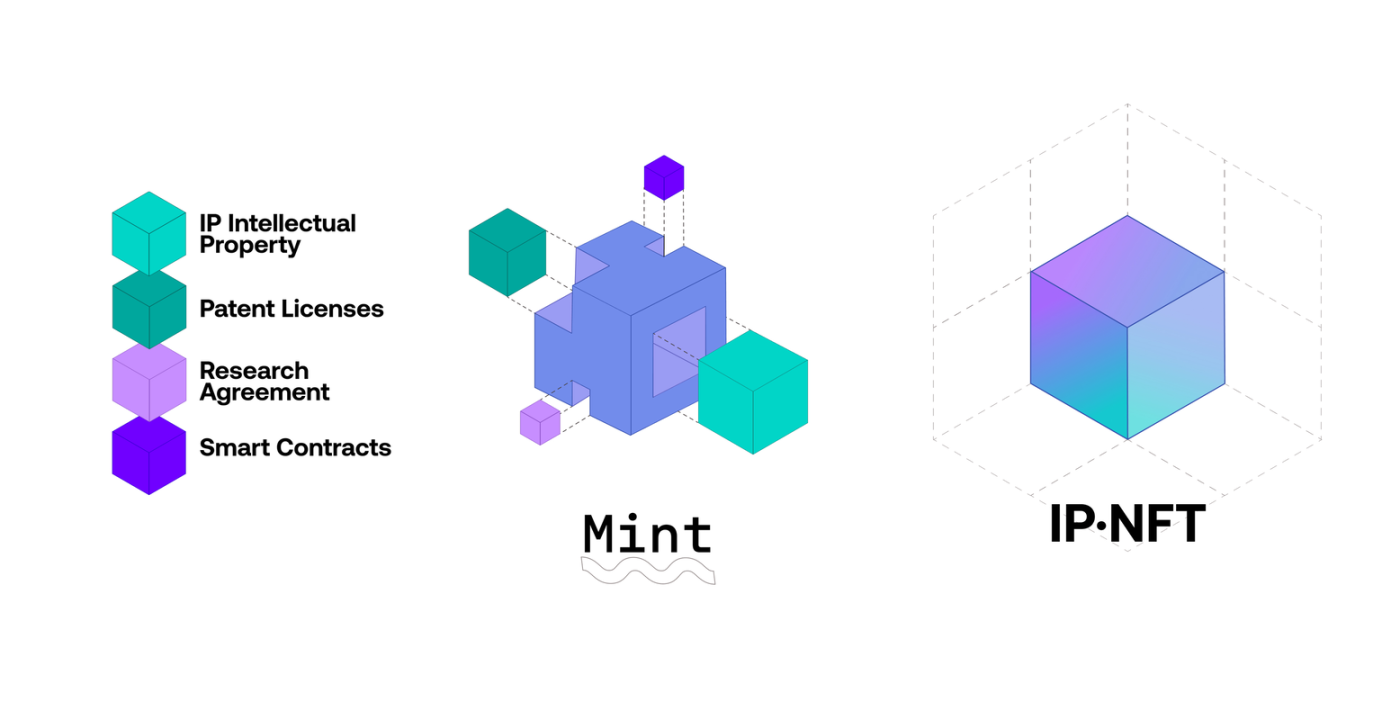
Figure 14: Generating IP NFT
IP-NFTs (Intellectual Property Non-Fungible Tokens) digitize intellectual property and manage it on the blockchain as non-fungible tokens. Each IP-NFT represents a specific piece of intellectual property, ensuring the uniqueness, transparency, and immutability of its ownership. This enables researchers to claim ownership, raise funds, and monetize intellectual property on the chain.
IPTs (Intellectual Property Tokens) are tokens carved out of IP-NFTs that represent a share of the intellectual property of a specific scientific research project. Holders can participate in the governance of intellectual property, including decision-making on research directions, resource allocation, and supervision of project progress. This tokenization mechanism makes intellectual property a tradable digital asset, promoting transparency and participation in scientific research.
By tokenizing intellectual property, Molecule makes the ownership of intellectual property publicly recorded on the blockchain, which can be queried and verified by anyone. This transparency reduces ownership disputes arising from multi-party cooperation and ensures that the rights and interests of all parties are clearly defined.
More importantly, the use of IP-NFTs and IPTs standardizes the management process of intellectual property and reduces the complexity caused by legal differences in different countries and regions. Through smart contracts, participants can collaborate on a unified platform, reducing legal barriers in international cooperation.
In addition, VitaDAO used the IP-NFT model to fund 15 anti-aging research projects in 2023, with a total amount of more than 4 million US dollars, effectively enhancing the control of scientific researchers over their results.
DAO: Making Science Transparent
In the field of decentralized science (DeSci), it is not difficult to find that many projects are named with "DAO", such as VitaDAO, BioDAO and CryoDAO. This naming method reflects DeSci's pursuit of the "Science 3.0 Spirit", that is, a more transparent, democratic and open way of scientific research.
DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) uses blockchain technology to build open, transparent and fair scientific research platforms. On these platforms, researchers can publicly display the research process, including experimental design, data collection and analysis methods. This transparent mechanism allows global researchers and the public to monitor and track project progress in real time, ensuring the verifiability and traceability of the scientific research process.
DAO's decentralized governance model gives more decision-making power to the scientific research community rather than traditional centralized management agencies. Community members participate in project decision-making by voting or holding tokens, realize the democratic allocation of scientific research funds, and reduce the bureaucracy and potential bias in traditional scientific research funding. This approach not only promotes the fair flow of resources, but also improves the diversity and inclusiveness of research projects.
DeSci emphasizes open science and encourages researchers to share data, methods and research results on decentralized platforms. This sharing method reduces scientific barriers, enables other researchers to reproduce experiments and verify results, reduces unnecessary repetitive experiments, and thus saves scientific research resources.
More importantly, the introduction of blockchain technology makes all data immutable and traceable, ensuring that scientific research records are authentic and reliable. In some DeSci projects, users who hold tokens or participate in community governance can access the project's scientific research database and directly review research data. Researchers receive financial incentives for sharing research progress (including failed experiments and negative results), thereby encouraging full disclosure of scientific discoveries. This mechanism effectively avoids the tendency of "publication bias" (publishing only successful experimental results) in traditional scientific research, ensures the integrity and comprehensiveness of scientific knowledge, and promotes the deeper development of science.
Through DAO and blockchain technology, DeSci not only redefines the scientific research funding model, but also promotes a more open, transparent and collaborative scientific ecosystem worldwide.
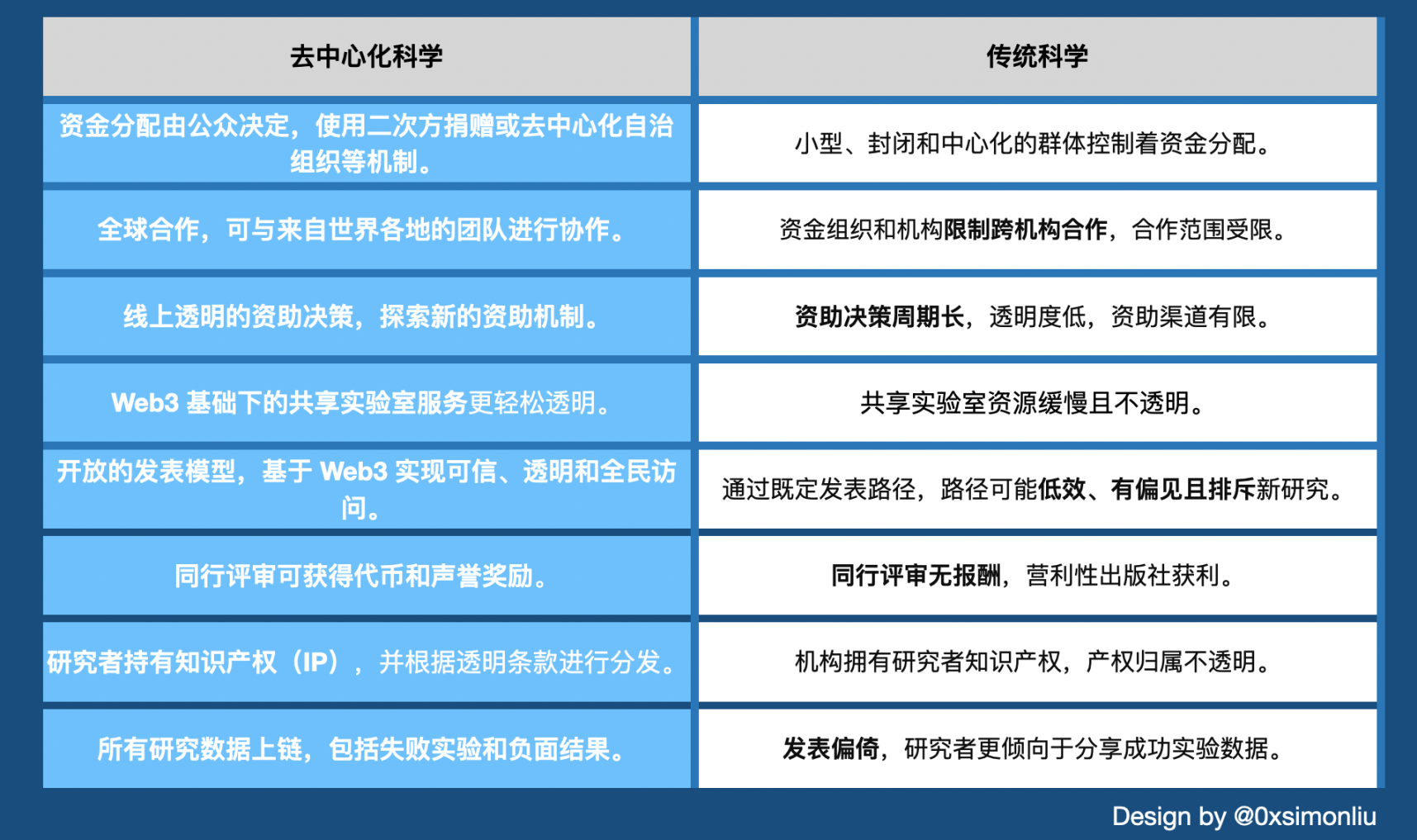
Figure 15: Comparison of decentralized science and traditional science
Conclusion: The inevitability of DeSci becoming an important narrative of Web3
Decentralized science (DeSci) is gradually becoming the core narrative in the Web3 ecosystem. Behind this is the result of the mutual promotion of science's demand for innovative technologies and Web3's exploration of real-world applications. This two-way drive has promoted the integration of scientific research and Web3 technology, promoted scientific research to develop in a more transparent, fair and efficient direction, and opened up new growth space for Web3.
The traditional scientific system has long faced problems such as uneven funding distribution, intellectual property monopoly, opaque scientific research process, and lack of incentives for peer review. A large amount of scientific research funds are concentrated in the hands of a few institutions and enterprises, which restricts the development of innovative projects. The opaque ownership of intellectual property rights makes it difficult for researchers to obtain rewards for their achievements, further inhibiting the diversity of scientific research. In addition, the lack of disclosure of failed experiments and negative results, as well as the unpaid peer review mechanism, have led to slow scientific research progress and serious waste of resources.
Web3 technology provides a solution to the above problems. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs), smart contracts, and token economic models make scientific research funding more democratic and transparent. Platforms such as Gitcoin and BioDAO allow the community to directly participate in funding through quadratic donations, and even small donations can be matched at high levels, which greatly promotes the development of innovative and small scientific research projects. Molecule uses IP-NFTs and IPTs to tokenize intellectual property rights, allowing researchers to directly hold and trade intellectual property shares, ensuring transparent property rights and bringing continuous benefits to researchers.
DeSci not only solves the core problems in scientific research, but also brings new growth momentum to Web3. At present, Web3 applications are mainly concentrated in DeFi, NFT and Metaverse, but there are few landings in the field of real infrastructure. DeSci introduces blockchain into fields such as scientific research and medical care, providing a new breakthrough for the application of Web3 in traditional industries. BioDAO has successfully funded multiple gene editing and precision medicine projects through the DeSci model, demonstrating the potential of Web3 in life sciences and social value.
With the rapid development of DeFi, some Web3 projects have been criticized by the outside world for speculation and bubbles, and the industry is facing negative perceptions. DeSci directly serves social and scientific progress, helps to reshape the social image of Web3, shapes it into an important force to promote human knowledge and medical innovation, and reduces the outside world's misunderstanding of the purely speculative nature of Web3.
The fundamental reason why DeSci has become an important narrative of Web3 is that it fills the gap between science and blockchain, and solves key issues such as funding allocation, intellectual property management, and scientific research transparency. At the same time, Web3 has found new application scenarios through DeSci, expanded the influence of technology, and promoted global scientific research into a new era of greater openness, efficiency, and democracy. The integration of DeSci and Web3 not only pushes scientific research into a more fair and transparent future, but also helps Web3 get rid of the stereotype of "speculative tools" and become a key force in promoting global innovation and social development.
Conclusion
The combination of DeSci and Web3 not only provides a new development path for scientific research, but also opens up a broad space for real-world applications for Web3 technology. DeSci is not only a transformative force for scientific research, but also an important bridge for cryptographic technology to move from financial tools to social infrastructure.
In the future, with the promotion and application of DeSci around the world, scientific research will enter a more transparent, democratic and efficient era, and Web3 will also achieve higher levels of social value and industry recognition through DeSci, helping global scientific research enter a new era of true openness, co-construction and sharing.
 Joy
Joy