High Court Dismisses Wright's Appeal in McCormack Case
The U.K. Supreme Court denies Craig Wright's appeal in his libel case against Peter McCormack, upholding a nominal 1 GBP damage award.
 Brian
Brian
The global financial system is undergoing a profound change, and at the center of this "financial upheaval" is not just Bitcoin or Ethereum, whose prices have skyrocketed or plummeted, but their seemingly low-key but crucial "stabilizer" - stablecoins.
These crypto assets, which are designed to anchor the value of legal currency, have quietly grown from marginal experiments to the core bridge connecting traditional finance and the crypto world, and their influence is deeply penetrating into the capillaries of the global economy.
Imagine: the cost and time of cross-border payments are reduced from days and tens of dollars to seconds and cents; people in emerging markets can avoid the sharp fluctuations of their own currencies and easily access US dollar assets; the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem has flourished due to the reliable value scale and exchange medium...
All of this, stablecoins are or will soon make it a reality. It is not only a "safe haven" for cryptocurrency transactions, but also shows subversive potential in reshaping the payment system, improving financial inclusion, and even challenging the role of traditional bank intermediaries.
The impact of stablecoins on the global financial economy and the future development directions worth paying attention to are as follows.
The Bitcoin Think Tank Bitcoin Research Institute published an article at the end of 2024 titled "Global Economic Restructuring: Sino-US Competition and Bitcoin as a Tool for American Governance", stating that in order to maintain its leadership in an increasingly competitive environment, the United States must adopt a forward-looking strategy to redefine the connotation of global economic participation. The strategy must integrate monetary, technological, industrial and geopolitical policies to address structural vulnerabilities, enhance the resilience of the US economy, and curb the ambitions of hostile forces.
At the heart of this potential geoeconomic strategy lies an entirely new monetary system—“Bretton Woods 3.0”—that combines the stability of traditional reserve assets such as gold and U.S. Treasuries with emerging financial instruments such as Bitcoin and dollar-backed stablecoins. By leveraging these assets, the United States can modernize its financial architecture, stabilize its fiscal position, and bolster trust in the dollar system. Instruments such as long-term bonds, strategic gold revaluations, and expanded swap lines will bind allies more closely to a U.S.-centric financial network while creating a buffer against fragmentation.
First, with stablecoins, the United States is working to usher in a new era of digital finance.
The U.S. "Forbes" magazine published an article on March 27, 2025 titled "Trump's Stablecoin Strategy Will Consolidate the Dominance of the Dollar", stating that in 1944, the Bretton Woods Agreement placed the dollar at the center of global finance. Today, a new change is taking place - not in closed-door meetings at ski resorts, but in GitHub repositories and smart contracts.
With stablecoins, the United States is committed to leading a new era of digital finance - the dominance of the dollar is consolidated not only by historical heritage, but also through new strategic and forward-looking public policies, and bold business and technological innovations led by the private sector driven by market competition.
The magazine also stated that the "Guidance and Establishment of the U.S. Stablecoin National Innovation Act" is not only a regulation, but also the basis for building a new blockchain-based dollar system. If the bill is passed, the dollar will expand further-not only through banks and borders, but also through encrypted wallets and codes.
Second, stablecoins provide a possibility to reshape the way funds are stored and moved across borders.
The U.S. "Forbes" magazine published an article on March 27, 2025, stating that research by consulting firm McKinsey showed that the global financial system holds $117 trillion in bank deposits, including $65 trillion in personal deposits. Stablecoins provide a possibility to reshape the way funds are stored and moved across borders.
By supporting stablecoins licensed and regulated by the United States and denominated in U.S. dollars to operate outside the traditional banking system, the United States is empowering an existing alternative global capital flow channel that may begin to effectively supplement or even partially replace traditional bank deposits.
Third, the rise of stablecoins backed by the U.S. dollar may consolidate the dominance of the U.S. dollar for decades or even longer.
Bloomberg News published an article on February 12, 2025 stating that every half a century or so, the world monetary order undergoes profound changes, and now may be witnessing the latest monetary revolution: the rise of stablecoins backed by the U.S. dollar may consolidate the dominance of the U.S. dollar for decades or even longer.
The simplest scenario is that people outside developed countries increasingly use stablecoins. The economies of these economies will be partially "dollarized/stablecoinized". People in these economies will become more accustomed to thinking and calculating in US dollars, even in domestic transactions. Dual-currency economies may become more common, with both national currencies and stablecoins backed by the US dollar.
Over time, due to concerns about the redemption risks brought by stablecoins, many countries will choose to completely dollarize, whether in whole or in part. In some cases, the US dollar may eventually dominate.
South Korea's Daily Economic News Network published an article on May 30, 2025, stating that as dollar-based stablecoins dominate the market, the daily use of US dollar settlements on the user side may become a potential problem. In virtual currency exchanges around the world, the US dollar has become the benchmark price centered on USDT and USD coin.
If stablecoins spread to ordinary settlement networks, ordinary domestic retail stores can also use the US dollar as the benchmark price for settlement. For countries that use their own currencies, it is likely to pose a serious threat to monetary sovereignty.
The World Economic Forum released a white paper titled "Macroeconomic Impacts of Cryptocurrencies and Stablecoins" in 2022, stating that the macroeconomic impact of stablecoins depends on the support behind them. For example, a stablecoin backed by bank deposits merely converts one form of money into another; whereas a stablecoin backed by securities may, in addition to being a "store of value," also be converted into a "medium of exchange," thereby achieving "money creation" in a sense.
This white paper focuses on stablecoins backed by fiat currencies and analyzes three high-level paths that countries may choose in regulating fiat stablecoins.
The first scenario: Allowing current trends to continue.
This strategy means not taking regulatory action immediately, but waiting for more information before making a decision. This could lead to adverse events before formal regulation is introduced. Some economists believe that this option is the least economically favorable because it fails to meet several core criteria.
Table 1 Impact of the “Let the current trend continue” scenario
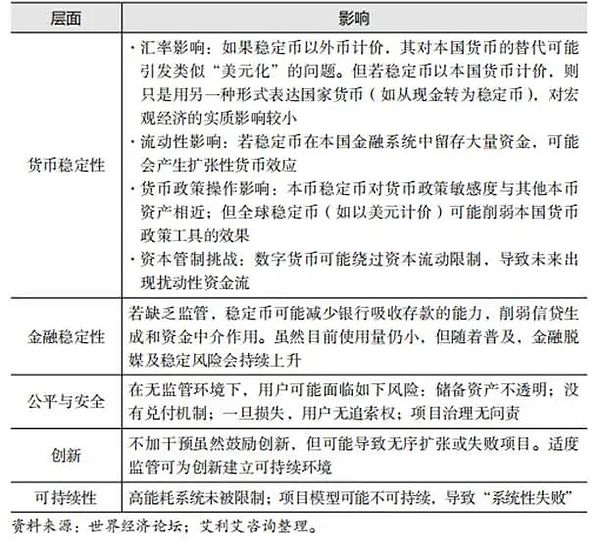
Second scenario: Allowing fiat-backed stablecoins to play a regulated role in the economy.
Strategy recommendations Establish rules to allow stablecoins to operate under a regulated framework, such as in payment, remittance and other fields.
Table 2 "Allowing fiat-backed stablecoins to play a regulated role in the economy" scenarios and requirements and recommendations
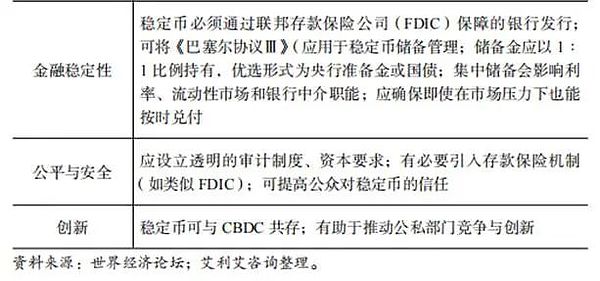
The third scenario: private fiat-backed stablecoins are driven out of the market through taxation or bans.
Table 3 Requirements and recommendations for the situation of "driving private fiat stablecoins out of the market through taxation or bans"
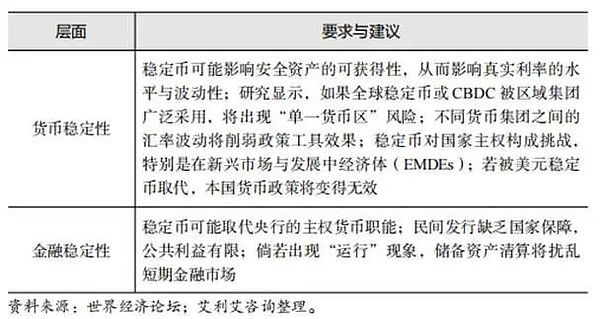
First, stablecoins are more closely connected to the broader financial system.
The stablecoin market has long seemed to be a logical connection point between the two worlds. The Wall Street Journal published an article on May 23, 2025, saying that the traditional giants of Wall Street are likely to join forces to issue their own stablecoins, which is the latest sign that mainstream finance and cryptocurrency finance are gradually moving closer. Given that stablecoins are used as an efficient way to transfer funds, the stablecoin market has long seemed to be a logical connection point between the two worlds.
The IMF pointed out in a 2022 article that stablecoins are not without potential risks. Being backed by financial assets means that they are more closely tied to the broader financial system than unbacked cryptocurrencies. If faced with liquidity pressures, stablecoin issuers holding reserve financial assets may be forced to sell these assets in large quantities, which could have an impact on the financial system. Although the impact of this risk transmission to the financial system is currently small, the relevant parties are developing regulatory tools that can be used in the event of significant risks.
On June 5, 2025, the US stablecoin issuer Circle successfully listed on the New York Stock Exchange with the stock code "CRCL". On the first day, the stock price soared from the issue price of US$31 to US$83.23, an increase of 168%. The company's market value exceeded US$18.3 billion, making it the second largest listed crypto company after Coinbase. The IPO raised a total of approximately US$1.1 billion, and underwriters included Wall Street giants such as JPMorgan Chase, Goldman Sachs and Citi, showing the high attention of traditional finance to the field of stablecoins.
Circle's successful listing is not only a milestone in its own development, but also marks the entry of the stablecoin market into the mainstream financial system. It is also another integration of cryptocurrency and real financial markets after the launch of Bitcoin ETF in January 2024. As a stablecoin issued by Circle, USD Coin currently has a market value of approximately US$61.5 billion, making it the world's second largest stablecoin after Tether.
Since its launch in 2018, USD Coin has supported more than US$25 trillion in on-chain transactions, with a transaction volume of US$6 trillion in the first quarter of 2025, showing its wide application in global payments and financial services.
Second, not all stablecoins are stable.
Global rating company Moody's published a research report titled "Stablecoins have always been unstable, why?" at the end of 2023, pointing out that there have been many driving factors for the decoupling of stablecoins in recent years. The main factors include the lack of regulation of large cryptocurrency exchanges, governance and risk management issues, pressure within traditional finance, and the imbalance of digital asset pools that provide liquidity for decentralized exchanges.
Stablecoin issuers face sources of instability that may lead to runs and bankruptcies. The European Banking Authority (EBA) issued a paper in August 2024 titled "Run Risk, Transparency and Regulation: On the Optimal Design of a Stablecoin Framework", pointing out that stablecoin issuers face sources of instability that are similar to those of the traditional banking system and may lead to runs and bankruptcies.
First, stablecoin holders (just like bank depositors) may redeem their stablecoins at unexpected times, which means that the issuer can easily become illiquid if a run occurs and a sufficiently high proportion of its reserve assets are not invested in liquid instruments.
Second, bankruptcy can be caused by a run or an exogenous shock that affects the value of the reserve asset portfolio. Although overcollateralization can reduce such risks, the possibility of bankruptcy cannot be completely eliminated if the reserve assets suffer a negative shock.
The Brookings Institution of the United States pointed out in an article published on May 8, 2025 that from the perspective of financial stability, if the value of stablecoins lacks real stability, it may trigger the risk of bank runs; if their operating system cannot cope with a variety of operational or cybersecurity threats, it may also weaken the security of the payment system. In addition, due to the rapid expansion potential brought by network effects, stablecoins may pose greater risks to credit intermediation and monetary policy transmission mechanisms - especially when a large amount of deposits from insured depository institutions flow into stablecoins; if stablecoins are issued by commercial companies, it may also lead to excessive concentration of market power.
The market is volatile, and despite the name of stablecoins, their volatility is extremely high. The US "Fortune" magazine published an article on May 15, 2025, stating that despite the name of stablecoins, their volatility is extremely high. Their trading value fluctuates violently, and some even plummet.
More importantly, if the U.S. Congress approves the weak government regulatory system set forth in the current proposed legislation, this will give stablecoins a deceptive legitimacy. As consumers withdraw bank deposits and money market fund assets to purchase stablecoins, reducing the funds available to banks and funds to finance American businesses and households, financial stability as a whole could be threatened.
The IMF published a paper in September 2022 titled "Stablecoins Are a Far cry from the Revolutionary Ideas of Crypto Asset Pioneers and Are Not Without Risks," pointing out that, in fact, most stablecoins fluctuate around their expected value rather than always maintaining it. Some stablecoins may deviate significantly from their expected value.
This is especially true for algorithmic stablecoins. Such tokens are designed to stabilize their value through an algorithm that adjusts issuance based on demand and supply, and are sometimes backed by unsecured crypto assets.
However, such tokens are extremely risky. The past experience of the algorithmic stablecoin TerraUSD shows that algorithmic stablecoins can easily decouple from their expected value if a huge shock occurs, and the process will continue once it starts.
Third, the integration of stablecoins into the traditional payment system can unleash the next wave of payment innovation.
The Czech World Press Syndicate published an article on March 24, 2025, stating that digital assets are expected to fully upgrade the 20th century financial system. Integrating stablecoins into traditional financial markets can unleash the next wave of payment innovation. The Trump administration and the current Congress seem to recognize that the digital transformation of money and finance is an inevitable trend. Now they must take responsibility for shaping the future of stablecoins and ensuring their security, so as not to give away the benefits.
The Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta, USA, issued a document on January 13, 2025, stating that the future of stablecoins as a payment method is still being explored, but as digital assets gain wider acceptance, their application scope may be further expanded, and may even be comparable to credit or debit cards. However, risks remain, including concerns about the stability of their supporting assets, regulatory uncertainty, and security vulnerabilities such as cyber attacks.
Despite these challenges, continued development and regulation will shape the future of stablecoins in the payment field. Although it is difficult to predict whether stablecoins will become a universal payment method, their foundation is being formed. Stablecoins, once seen as a tool to hedge against cryptocurrency fluctuations, are now gradually becoming an innovative payment method.
The Financial Times of the United Kingdom published an article on May 7, 2025, "Stablecoins should be regarded as a currency", saying that stablecoins are now facing challenges similar to those of paper money in 18th century England.
Stablecoins have been proven to have the main characteristics of currency: accounting units, means of storing value and medium of exchange, and the total value of stablecoins in circulation has reached US$240 billion. However, the recent US "Guidance and Establishment of a National Innovation Act for Stablecoins in the United States" and the "Stablecoin Act" have not clearly defined stablecoins as currency under private commercial law, tax law and accounting rules.
First, potential property claims by previous owners could hinder the use of stablecoins.
This case of stolen banknotes in 18th-century England is an important cornerstone of the American payment law system. Lord Mansfield’s ruling is enshrined in the “sound acquisition rule” in the Uniform Commercial Code, the law that governs commercial transactions. In 2022, the code
added Article 12 to deal with digital assets. If stablecoins are considered “controllable electronic records,” the “sound acquisition rule” of Article 12 applies—meaning that the rights of upstream creditors will be cut off.
However, only 27 states in the United States have adopted Section 12 so far. For the remaining states, stablecoins may be considered "general intangible assets", which means that previous property claims may continue to be attached to them, making them a poor medium of exchange.
Second, how stablecoins are treated under tax rules is equally important.
Deloitte, a well-known global accounting firm, published an article on March 18, 2025 stating that although stablecoins can be used as a means of payment and have a value similar to fiat currency, they may not be considered currency for US income tax purposes. Instead, depending on the structure of stablecoins and the interpretation of existing US Treasury regulations enacted before the emergence of blockchain and digital assets, stablecoins may be considered general property or even debt obligations. In addition, payments using stablecoins may be subject to the same information reporting requirements as other digital assets.
The Financial Times noted that if stablecoins continue to be classified as "property" like digital assets such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, their gains and losses must be reported to the IRS. As stablecoin payments become more widely used, millions of personal and commercial payment reports may be submitted to the government. In addition, if stablecoins are used to purchase goods, this may be considered a "disposition event" subject to capital gains tax, and bring cumbersome and confusing tax treatment issues to consumers and businesses.
One way to solve the problem is to ensure that stablecoins are always bought and sold at a value that is exactly equivalent to currency - meaning there are no gains or losses. To do this, stablecoin legislation must require issuers to follow strict reserve requirements to ensure currency stability, as well as asset isolation requirements to defend against creditors in the event of the issuer's bankruptcy. Another way is for Congress to reduce tax reporting requirements. There is already a precedent - personal foreign exchange trading income of less than $200 is exempt from reporting.
Third, it is still unclear whether stablecoins should be reported as cash equivalents or financial instruments under accounting rules.
Accounting rules will also become important as stablecoins become more common in traditional commerce, according to the Financial Times. It is still unclear whether stablecoins should be reported as cash equivalents or financial instruments under accounting rules. The way they are classified will have a significant impact on how companies report their holdings of stablecoins and their use. Ultimately, if stablecoins are not clearly defined as a form of currency - either as cash equivalents or negotiable notes - it could make them lose their practicality as a medium of exchange and could make potentially important legislation meaningless.
Deloitte, a world-renowned accounting firm, published an article on March 18, 2025, stating that from an accounting perspective, stablecoin holders need to evaluate terms to determine whether these stablecoins represent financial assets or intangible assets, which will affect classification, subsequent measurement, and accounting treatment of subsequent transfers. For stablecoins that are identified as intangible assets, entities also need to consider whether such assets fall within the scope of the new accounting guidelines for crypto assets under the U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (US GAAP), including new mandatory disclosure requirements. Finally, for entities that are issuers of stablecoins, it is necessary to determine whether these stablecoins represent financial liabilities.
First, stablecoins may challenge the comprehensiveness and effectiveness of existing regulatory and supervisory mechanisms.
The Financial Stability Board (FSB) published an article at the end of November 2024 stating that there is currently no generally accepted legal or regulatory definition of stablecoins. Stablecoins are usually created and issued through trading platforms in exchange for fiat currencies. Issuers of stablecoins can use the proceeds of fiat currencies to invest in reserves or other assets. In its 2020 report "Regulation, Supervision and Review of Global Stablecoin Arrangements", the FSB described three characteristics of global stablecoins (GSCs) that distinguish them from other crypto assets and stablecoins.
The FSB said that the emergence of GSCs may challenge the comprehensiveness and effectiveness of existing regulatory and supervisory mechanisms. The FSB has agreed on 10 high-level recommendations, which were revised in July 2023, to promote consistent and effective cross-jurisdictional regulation, supervision and review of GSCs and stablecoins that may become GSCs to address the financial stability risks they pose to the domestic and international levels.
Table 4 Three characteristics of global stablecoins that distinguish them from other crypto assets and stablecoins
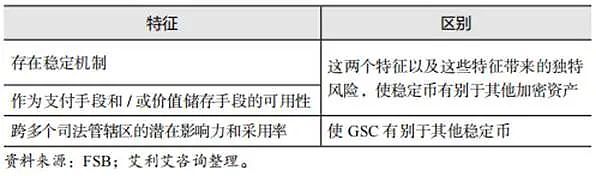
The Journal of International Economic Law, published by Oxford University Press in the UK, published an article on May 21, 2025 entitled "Stablecoins and Their Regulation: Hayek's Perspective", stating that, as reflected in emerging regulatory approaches, regulators are particularly cautious about so-called systemic or global stablecoins, which have huge trading volumes and important connections with off-chain markets in the real world. In addition to challenging the status of the banking system, the large-scale use of stablecoins as a substitute for fiat currencies will significantly limit the ability of countries to implement monetary policy through interest rates.
It is widely believed that it was Facebook's Libra project - "the first "global stablecoin proposal for retail payments" supported by a corporate group" - that prompted regulators to put stablecoins at the top of their regulatory priorities. Given Facebook's large social media network and its existing payment infrastructure (including Facebook Pay, WhatsApp Pay and Instagram Pay), it would have been relatively easy for Libra to achieve the global stablecoin status that regulators were worried about. Although the Libra project seems to have been abandoned for now, stablecoins offered by other organizations with payment infrastructure (such as PayPal) may be equally risky in the eyes of regulators.
Systemic stablecoins may also endanger the monetary sovereignty of countries. If a large number of citizens use a stablecoin pegged to another country's currency, the monetary policy of the pegged currency will have an excessive impact on the economy of the country using the stablecoin. This is particularly true for developing countries with unstable economies, but developed countries that issue major reserve assets are also concerned about monetary sovereignty issues, because a potential run on a systemic stablecoin could jeopardize the stability and value of its pegged reserve assets.
Other potential risks of stablecoins include market concentration issues, especially when stablecoin providers are vertically integrated and also provide custody or other crypto-related services. PayPal is an example of this, as it provides both stablecoins and payment networks as well as crypto asset trading and custody services.
Second, 6 stablecoin development directions worth paying attention to.
Foresight News, a news and research organization focusing on blockchain and digital assets, published an article on June 3, 2025, pointing out that stablecoins, as a financial innovation driven by blockchain technology, are at a critical turning point from wild growth to standardized development. While global regulators recognize its huge potential, they are also highly concerned about the risks it brings.
In the future, a clear and adaptable regulatory framework will be an important guarantee for stablecoins to play a positive role in payment modernization, financial inclusion and digital economic development. Its development is not only about technology and markets, but also deeply rooted in the evolution of the global economic landscape and national strategies. Foresight News pointed out that there are 6 development directions of stablecoins in the future that deserve attention.
First, the necessity and challenge of global regulatory coordination. The cross-border nature of stablecoins requires strengthening international regulatory cooperation to prevent regulatory arbitrage and systemic risks, but differences in interests and capabilities among countries pose challenges.
Second, the entry of large technology companies and traditional financial institutions. The cautious attitude of regulators towards the issuance of stablecoins by large technology companies and the active participation of traditional financial institutions will jointly shape the competitive landscape of the stablecoin market. Among them, Visa has participated in the investment of part of the upstream and downstream infrastructure related to stablecoins, while PayPal chose to cooperate with Paxos to issue its own stablecoin PayPal USD.
The Wall Street Journal published an article on May 23rd, saying that the largest banks in the United States are exploring the cooperation to issue a joint stablecoin, a move aimed at fending off the growing competition from the cryptocurrency industry. People familiar with the matter revealed that so far, the companies involved in the discussion include companies jointly owned by JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America, Citigroup, Wells Fargo and other large commercial banks.
The third is the combination of stablecoins and real-world assets (RWA). Compliant stablecoins will become the key pricing and settlement tools for RWA circulation on the chain, and its regulatory implementation is expected to give rise to a new round of innovation around RWA tokenization.
Fourth, the evolution of the "onshore" and "offshore" stablecoin systems. With the tightening of regulation in major economies, there may be a situation where the strictly regulated "onshore" system and the "offshore" system with a more diverse and complex ecosystem coexist.
Fifth, innovation in stablecoin + payment + AI. Advances in artificial intelligence may be deeply integrated with stablecoin payments, such as AI-driven automated transactions, complex payment logic executed by smart contracts, and applications in the machine-to-machine (M2M) and AI agent-to-agent (A2A) economies, bringing unprecedented intelligence and efficiency to payments.
Sixth, the continuous interaction between technological innovation and regulation. Stablecoin technology (such as integration with DeFi, Layer2 solutions) is still iterating rapidly, and regulation needs to remain adaptable, effectively managing emerging risks while encouraging innovation.
Third, the key to winning the stablecoin war lies not in technological advantages or first-mover status, but in the application ecosystem.
The Harvard Business Review published an article in 2024 titled "The Race for Stablecoin Dominance," stating that the key to winning the stablecoin war lies not in technological advantages or first-mover status, but in the application ecosystem. Although regulators may significantly raise the competitive threshold for innovators, they can never completely stifle innovation.
The final situation is likely to be that diversified stablecoins will be hidden behind the scenes, providing lower-cost and faster payment services to the world. This is a win-win situation for consumers and businesses - although this may not be the case for existing stablecoin issuers, as they may eventually be taken over by banks.
The magazine also said that when the dust settles, the battle for digital wallets will not end. The giants will still compete for control of the "payment entrance": credit card organizations are bound to stick to the "Visa/MasterCard payment" process position (the banking system is happy to see this), and the real mission of breaking the deadlock will fall on the shoulders of new digital banks and cryptocurrency exchanges. Only they can initiate disruptive innovation and become a force that rewrites the rules of the game.
German consulting firm Roland Berger published an article on March 4, 2025 titled "Stablecoins - The Future of Money", pointing out that to truly enter the mainstream, stablecoins need to be as simple and easy to use as mainstream consumer applications such as WhatsApp. Until recently, the poor user experience of digital asset wallets was a key constraint on the adoption of stablecoins. However, new digital asset wallets such as Phantom have proven that significant improvements in user interfaces will in turn drive further adoption.
Fiat channels are also critical to driving adoption. Although it is now cheap and easy to transfer stablecoins point-to-point across borders, this is not enough to enable remittances. Users still need a way to convert stablecoins into fiat currency - and this is where there is a major bottleneck. To solve this problem, a fiat channel is needed.
The rapid development of digital technology and its deep penetration into daily life have provided new opportunities for alternative monetary systems other than fiat currencies, challenging the existing financial and monetary systems. Among various crypto assets, stablecoins are most likely to become the actual medium of exchange.
Although stablecoins meet some of the conditions in Hayek's vision of a competitive monetary system, they have not yet fully met them. Although still in its early stages, blockchain technology has provided a platform for the design of a variety of alternative models - such as decentralized and centralized, algorithm-driven and collateral-backed, anchored to fiat currencies and anchored to other assets. This emerging market has attracted a wide range of participants from small developers to multinational giants, and has also provided consumers with a variety of choices, each with its own advantages and risks.
Looking at the historical context of financial development, its essence is a profound change driven by technological evolution and institutional innovation, which continues to expand the boundaries of economic growth and the space for human well-being. In the context of the clear infrastructure route of blockchain technology, stablecoins, as an important link and key bridge connecting the digital world (cryptocurrency) and traditional finance, are becoming a strategic high ground for a new round of competition.
The significance of stablecoins lies not only in providing a price anchor for crypto assets, but also in their systematic potential in improving payment efficiency, reducing transaction costs, and expanding the accessibility of financial services. For the vast number of people who have not yet fully integrated into the modern financial system, stablecoins are expected to bridge the inclusive financial gap in a digital way; and their programmability provides a technical path for building a flexible and efficient new financial infrastructure. This is not only about the evolution of financial products, but also about the reconstruction logic of the future financial system.
However, the release of technological potential must rely on the support of the institutional framework. Only under a sound regulatory system can the development of stablecoins be sustainable, controllable and governable. This includes effectively strengthening consumer rights protection, strictly implementing anti-money laundering and anti-terrorist financing obligations, properly handling the relationship between monetary sovereignty and financial stability, and promoting international regulatory coordination and optimization of the competitive ecology.
From a broader perspective, the development of stablecoins is not only part of the evolution of financial technology, but also a key variable in the process of reconstructing the global financial order. Its direction will profoundly affect the future pattern of the payment system, the development path of the digital economy and even the strategic layout of national financial security.
The future currency game has surpassed the traditional financial territory and is deeply integrated into the historical process of the evolution of digital civilization. This competition for the dominance of stablecoins is not only a technological revolution in the transition of currency form from physical sovereign credit to algorithmic credit, but also a full-dimensional reconstruction of the financial sovereignty of major countries in the digital space.
Looking to the future, the story of stablecoins is still being written. Only on the basis of a virtuous interaction between policy governance and technological innovation can we ensure that it truly serves the overall situation of my country's economic development and the high-quality transformation of the financial system. The development direction of the next stage depends not only on the continuous exploration of market players, but also calls for policy responses and institutional designs with a forward-looking, systematic and global perspective.
The U.K. Supreme Court denies Craig Wright's appeal in his libel case against Peter McCormack, upholding a nominal 1 GBP damage award.
 Brian
BrianSwan Bitcoin expands into mining, targets public trading, emphasizes financial prudence, and forges strategic partnerships, all while navigating the uncertain waters of market dynamics and regulations.
 Weiliang
WeiliangJPMorgan's analysis points to a potential stabilisation in Bitcoin's valuation, post the GBTC sell-off whirlwind. The market's next moves, while uncertain, are watched with a keen, analytical eye.
 Miyuki
MiyukiBONK and WIF, memecoins on the Solana blockchain, experience dramatic shifts in market positions, reflecting the volatile nature of the crypto market.
 Brian
BrianU.S. prepares to auction $130 million in Bitcoin, seized from dark web dealings, showcasing the intricate dance between digital innovation and law enforcement.
 Weiliang
WeiliangNigeria's Central Bank, under new leadership, embarks on significant economic reforms focusing on inflation and currency stabilization.
 Miyuki
MiyukiJoe Lewis, a notable figure with ties to FTX and Tottenham Hotspur, pleads guilty to insider trading charges in a US court.
 Brian
BrianDespite offering a $4.5 billion stake in Binance as collateral, the judge turned down Zhao's plea, marking another setback for the cryptocurrency exchange mogul.
 Alex
AlexSu Zhu, co-founder of the collapsed Three Arrows Capital, labels his prison time as "enjoyable" and shifts focus to a cryptic exchange, OPNX, linked to Hong Kong. The unusual prison revelation and OPNX's connection to the regulatory landscape in Hong Kong add a unique twist to Zhu's crypto journey.
 Joy
JoyChinese investors, facing economic uncertainty, are turning to cryptocurrencies and overseas markets, with a surge in crypto activity despite regulatory bans. The growing interest signals a notable shift in investment strategies and a potential boom in China's overseas investment landscape.
 Joy
Joy