This article focuses on the U.S. Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for U.S. Stablecoins Act (hereinafter referred to as the "GENIUS Act" or the "Genius Act").
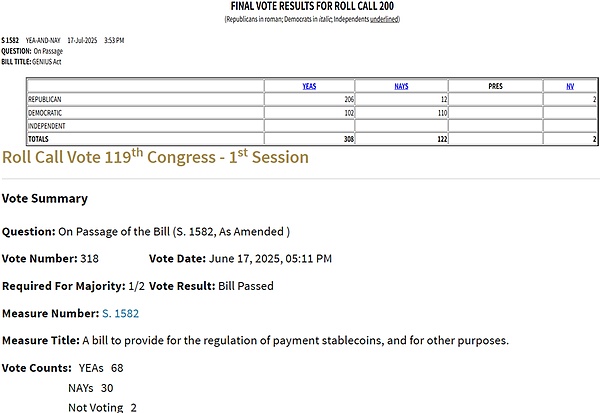
1. Event: The US "Genius Act" was finally passed
(1)2025Year7month
(2) "GENIUSAct" was sponsored by the Republican Senator from Tennessee. 2025In MarchMarch, the Senate Banking Committee passed the bill with a bipartisan vote of 186; leaf="">2025Year5Month19Day, the U.S. Senate voted in favor,32
2. What will happen next?
(I) Since the GENIUS Act was submitted in the form of a Senate bill and passed in the Senate on June 17, 2006, leaf="">Votes to30The bill was approved with 30 votes, which means that it only needs to be signed by US President Trump to become law. The market currently expects President Trump to sign the bill this Friday (local time in the United States).
(II) After the United States signs the "Genius Act", US regulators will begin to formulate relevant regulations on the behavior of stablecoin issuers, clarifying the specific details that stablecoin issuers and related digital asset service providers need to meet.
III. Main contents of the U.S. “Genius Act”
(I) Focusing on payment-type stablecoins and characterizing them as “digital assets”
The Genius Act aims to establish a regulatory framework for payment-type stablecoins (i.e., digital assets that issuers must redeem at a fixed value). This statement has two connotations:
1
1. It is clear that the regulatory object is payment-type stablecoins, which means that stablecoins with investment and financing nature are not included in its supervision, and only the payment and settlement function of stablecoins is focused on. 2. It is clear that payment-type stablecoins are digital assets, not digital currencies. 3. It is clear that payment-type stablecoins are digital assets, not digital currencies. 4. This actually further restricts the function of stablecoins, preventing stablecoins from becoming a tool for illegal fundraising or illegal deposit-taking, that is, the policy level attaches more importance to and encourages the payment and settlement function of stablecoins, and the attitude towards its investment and financing function is still ambiguous.
(II) Strict requirements for issuers
1. The bill specifies that stablecoin issuers must be "licensed payment stablecoin issuers", including insured depository institution subsidiaries, federally qualified non-bank issuers, or state-level issuers that meet federal standards. Among them, issuers with an issuance scale of more than 10 billion US dollars are subject to federal supervision, and smaller issuers can operate under a state-level framework that meets federal standards.
2, The issuer of stablecoins needs to meet bank-level compliance and regulatory requirements and must be subject to supervision by the Federal Reserve and the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, as well as the U.S. Secretary of the Treasury and the Stablecoin Certification Review Committee (newly established).
3In addition, foreign stablecoin issuers (such as Tether, the largest stablecoin issuer on the market) will also face restrictions on extraterritorial jurisdiction of the United States (especially if there is issuance or sales within the jurisdiction of the United States). In other words, foreign issuers such as Tether will face the same regulatory framework as U.S. stablecoin issuers.
This regulation is equivalent to clarifying the licensing system and regulatory system for stablecoin issuers, limiting the stablecoin ambitions of large technology companies (making them subject to constraints). It should be noted that, slightly different from banks, the US Treasury plays a greater role in the regulation of stablecoins (for example, it can designate unqualified foreign issuers and restrict their entry into the US market, etc.).
(III) Strict requirements for reserves: at least 100%+prohibition of re-mortgage+monthly public disclosure of information
1The bill proposes that stablecoin issuers must hold
leaf="">100%of high-quality liquid assets as reserves, which include but are not limited to (1) U.S. dollars, bank deposits; (3The bill also requires that the above reserves be segregated from the issuer's own funds and that information be disclosed and audited publicly on a monthly basis, such as publishing the monthly reserve composition (including the total number of outstanding stablecoins, the amount and composition of reserves, the average term of each type of reserve instrument and the custodial geographical location, etc.) on the issuer's official website.
(IV) Strengthening consumer protection: Stablecoin holders are required to have priority claims, and yield-based stablecoins are prohibited, etc.
1. Issuers are required to establish clear and eye-catching procedures for timely redemption of outstanding stablecoins.
2. Stablecoin holders are required to have priority claims when the issuer goes bankrupt, and false advertising is prohibited.
3, It is prohibited to promote stablecoins as assets with returns or government endorsement.
4, Require issuers to comply with anti-money laundering, anti-terrorist financing and other compliance requirements.
Four. Pay attention to two bills other than the Genius Act
(a) The U.S. House of Representatives passed two other bills on the same day that the “Genius Act” was passed
On the same day that the “Genius Act” was passed, the U.S. House of Representatives also passed two other bills:
1
2
3
4
5 text="">294votes134votes passed "Digital Asset Market Clarity Act of 2025, referred to as "CLARITY Act》), 78Democrats voted in favor.
2, passed the Anti-CBDC Surveillance State Act by a vote of 219 to 210. Some people say that these two bills have supported the Democrats to embrace the genius bill to a certain extent, but the strange thing is that the number of Democrats who voted in favor of these two bills is not large. (2) Main contents of the Digital Asset Market Clarity Act of 2024 The CLARITY Act establishes a clear and unified regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies, tokens and other digital assets by clarifying the classification, regulatory responsibilities and compliance paths of digital assets. The main contents are as follows: 1. Digital assets are divided into two categories: digital commodities and digital securities. (1) Digital commodities mainly refer to assets with a high degree of decentralization, which do not meet the securities standards and rely on regional chains to realize their value (such as Bitcoin and Ethereum). Their characteristics are that they can operate without relying on the continuous efforts of the issuer, and their functions are closer to traditional commodities rather than investment tools.
(2) Digital securities refer to investment contracts that meetHowey Teststandards, or digital assets that are clearly issued as securities (such as token assets raised through token issuance, etc.).
《
23456789101112131415 The CLARITY Act clarifies the scope of regulatory responsibilities of the two major U.S. regulatory agencies in the field of digital assets, and proposes that a coordination mechanism can be established to avoid possible conflicts between the CFTC and the SEC over regulatory boundaries.
(1CFTC) is responsible for regulating digital commodities and transactions (including digital commodities, digital commodity exchanges, brokers and traders, etc.). At the same time, the bill clearly states that digital commodities must meet specific conditions before they can be traded on exchanges. These conditions include that the blockchain technology they rely on is relatively mature, the issuer of the digital commodity must submit specific reports, transaction monitoring and record keeping meet specific requirements, and customer assets cannot be mixed with the issuer.
(2) The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC
) is responsible for supervising digital securities, such as requiring issuers to register and disclose information and comply with anti-fraud regulations. At the same time, the bill also stipulates thatSECmay supervise the digital commodity activities and transactions conducted by specific brokers and traders in alternative trading systems. 3, other
"CLARITY Act" Other noteworthy contents include but are not limited to:
(1
(3)makes a series of provisions on taxation, anti-money laundering and consumer protection.
(4) proposes exclusive rules for stablecoins to avoid the risk of “decoupling” of stablecoins, such as100%reserve asset requirements, regular disclosure of reserves and third-party audit requirements.
(3) The main content of the “Anti-Central Bank Digital Currency Surveillance National Act”
The bill prevents the Federal Reserve from issuing central bank digital currency (CBDC) directly to individuals, in order to prevent the Federal Reserve from using digital dollars as a tool to monitor or control personal finances. The specific contents are as follows:
1. The Federal Reserve is prohibited from issuing CBDC directly to individuals or entities outside the banking system, which means that the Federal Reserve cannot create digital wallets or accounts for citizens to hold digital dollars.
2. The Federal Reserve is prohibited from using CBDCas a tool for implementing monetary policy. The background is that some people are concerned that CBDCmay be used to implement policy tools such as negative interest rates or direct stimulus payments.
3. Prohibit the Federal Reserve from conductingCBDCrelated pilot projects or research.
4Formally incorporate Trump's executive order opposing CBDCinto law, making the U.S. government's ban on CBDCa permanent feature of U.S. financial regulation rather than a temporary policy.
V. Conclusion
(I) Stablecoin issuers and stablecoins are equivalent to "shadow central banks" and "shadow currencies" respectively
1After the bill is officially implemented, stablecoin issuers and stablecoins will play a similar role as shadow central banks and shadow currencies, and promote the market to be standardized, enhance market confidence, and promote more issuers and investors to enter the stablecoin market. Because since ancient times, the competition for the right to issue currency has been very fierce.
2, Of course, this is only a relatively medium- to long-term thing. After all, from the current perspective, stablecoins are still limited to payment and settlement functions, and their investment and financing attributes are still intentionally restricted (such as it is clear that they cannot pay interest to holders like deposits).
(II) The reason behind “encouraging stablecoins on the one hand and strictly restricting central bank digital currencies on the other hand” is worth noting
1
The other two bills passed by the House of Representatives this time are also worth noting, especially the Anti-Central Bank Digital Currency Surveillance State Act. The bill’s ban on the Federal Reserve’s deep involvement in central bank digital currencies has puzzled many people. The superficial reason is to protect personal financial privacy and prevent the government from expanding its own power throughCBDC, but another reason is also worth noting, that is, to prevent or weaken the development of central bank digital currencies in other economies. 2, At present, the United States is encouraging stablecoins on the one hand, but strictly restricting central bank digital currencies on the other. This completely different orientation is obviously worthy of attention. I think the reason is simple. The former is conducive to consolidating the hegemony of the US dollar, while the latter is to curb the erosion of the hegemony of the US dollar by other economies with the help of digital currencies.
(III) The U.S. dollar really hopes to create more linked exchange rate markets like Hong Kong and Macao to consolidate the dollar hegemony
1

(III) The U.S. dollar really hopes to create more linked exchange rate markets like Hong Kong and Macao to consolidate the U.S. dollar hegemony
2
The “Genius Act” clearly states that stablecoins must have 100% 3
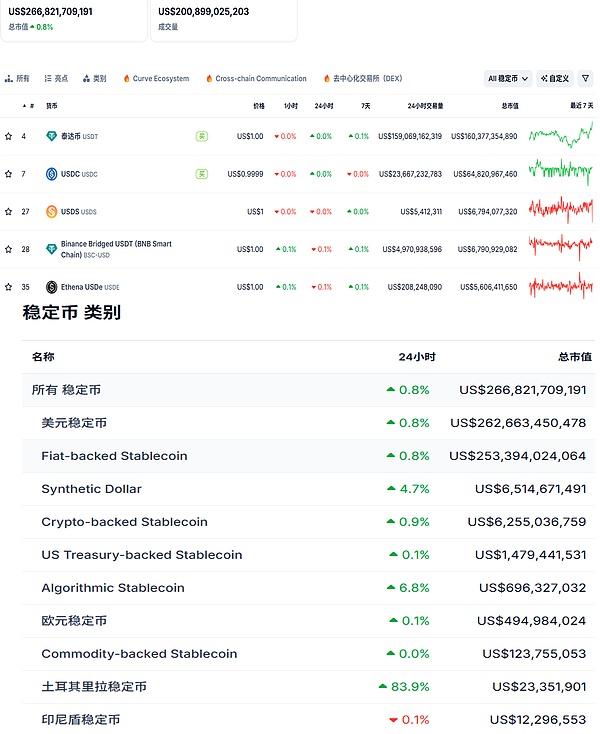
, Previously, relevant US personnel predicted that the size of the US stablecoin market will increase from the current 200 billionan average of 2t1020t3, Previously, relevant US personnel predicted that the size of the US stablecoin market will increase from the current 200 billion Hagerty even predicted that the issuer of stablecoins will become the "world's largest holder" of U.S. Treasury bonds in 2030, which shows that the United States has ambitions in the stablecoin market. Of course, this ambition does have support. At present, the total market value of stablecoins reaches 2668.22billion US dollars (Tether’sUSDT, Circle'sUSDC、USDShave a market value of US$160.4 billion, US$64.8 billion and US$6.8 billion respectively), plus some other dollar-pegged stablecoins, it is estimated that the share of dollar-pegged stablecoins in the entire market will reach (IV) The stable currency mechanism will, to a certain extent, exacerbate the "financial disintermediation" effect
1If we understand it in the logic of "shadow central bank" and "shadow currency", then the Yu'ebao launched by Alibaba and the WeChat Financial Management of Tencent also play a similar role to this kind of shadow currency or stable currency to some extent. In the environment of no supervision or weak supervision, the emergence of Yu'ebao and WeChat Financial Management made people begin to pay much more attention to "financial disintermediation", and their scale expansion in a short period of time has left a deep impression on bank practitioners to this day.
2From this perspective, the current regulatory framework for the stablecoin market is actually a form of protection for the financial industry. However, the emergence of Yu'ebao and WeChat Wealth Management did force the reform of China's banking industry to a certain extent. I think the same is true for the stablecoin market today, that is, the financial industry should take the initiative to embrace it and integrate it, rather than reject it.
 XingChi
XingChi






